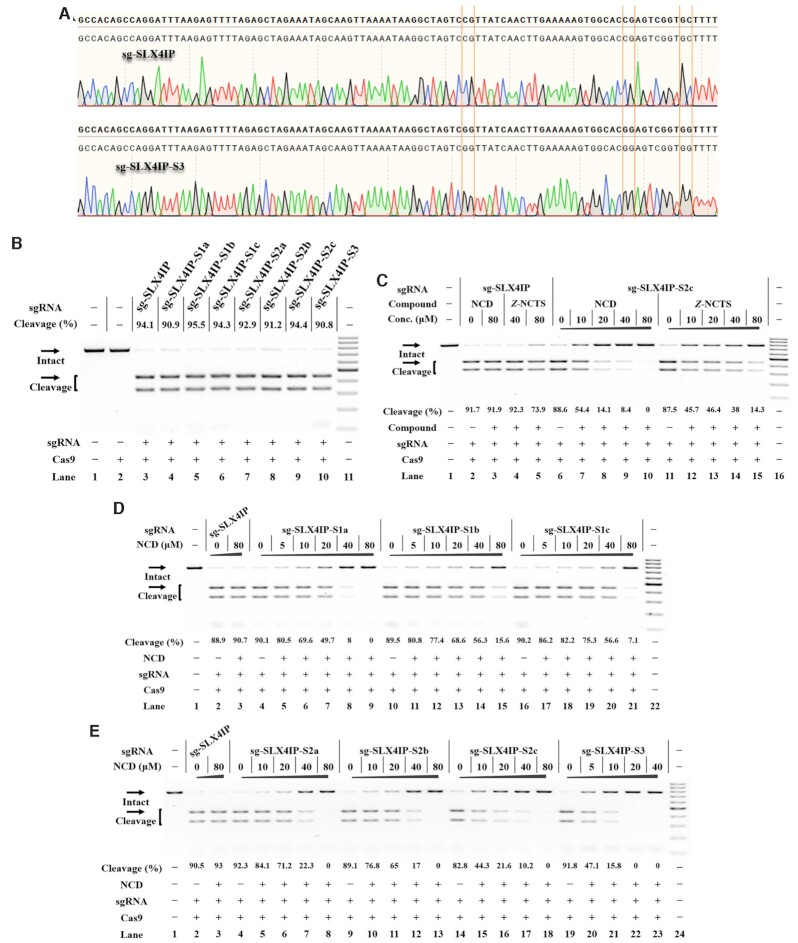
Figure 4.
Ligand control of designer sgRNAs for switching CRISPR/Cas9 Reactions were performed as described in the Experimental Section. Uncleaved SLX4IP DNA (773 bp) cut to shorter cleavage fragments (441 bp and 332 bp) are demonstrated. All samples were tested in three biological replicates. Image of representative data is shown here. (A) Sanger sequencing analysis of selected sgRNAs. The sites for sequence modification are indicated. (B) The tolerance of Cas9 to each designer sgRNA. Lane 1: target control; lane 2: Cas9-only control; lane 3 contains original sg-SLX4IP; lanes 4–10 contain designer sgRNAs harboring different MBL-binding units; lane 11: DNA marker (GeneRuler 100-bp DNA Ladder). (C) Responsiveness of designer sgRNAs to different MBLs. Lane 1: no Cas9 control; lanes 2–5 contain original sg-SLX4IP; lanes 6–10, 11–15 contain sg-SLX4IP-S2c; lane 16: DNA marker. (D) The NCD-dependent inhibition of CRISPR/Cas9 with single-site variants. Lane 1: no Cas9 control; lanes 2–3 contain original sg-SLX4IP; lanes 4–9 contain sg-SLX4IP-S1a; lanes 10–15 contain sg-SLX4IP-S1b; lanes 16–21 contain sg-SLX4IP-S1c; lane 22: DNA marker. (E) The NCD-dependent inhibition of CRISPR/Cas9 with multi-nucleotide variants. Lane 1: no Cas9 control; lanes 2–3 contain original sg-SLX4IP; lanes 4–8 contain sg-SLX4IP-S2a; lanes 9–13 contain sg-SLX4IP-S2b; lanes 14–18 contain sg-SLX4IP-S2c; lanes 19–23 contain sg-SLX4IP-S3; lane 24: DNA marker.