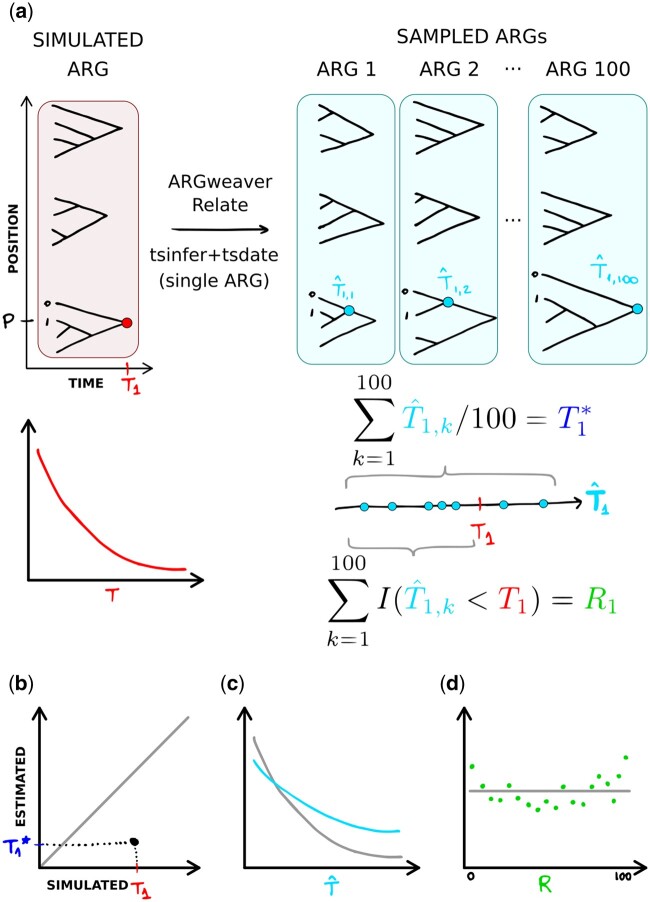
Fig. 2.
Methods overview. a) Data (ARGs and DNA sequences) were simulated from the coalescent with recombination. In the model and simulated data, pairwise coalescence times (CT) are exponentially distributed (Supplementary Fig. 3). T1 represents the CT between samples 0 and 1, at position P in the simulated data. is the CT between samples 0 and 1 at position P, in each ARG sample k. Point estimates are obtained as the mean of , and the rank statistic is computed as the number of that are smaller than the true value T1. b) We compare estimated to simulated values of the CT of each pair of samples, at each position of the genome. c) We compare the distribution of sampled CT across all sampled ARGs, all sites and all pairs of samples to the expected exponential distribution. d) We compare the distribution of ranks to the expected uniform distribution.