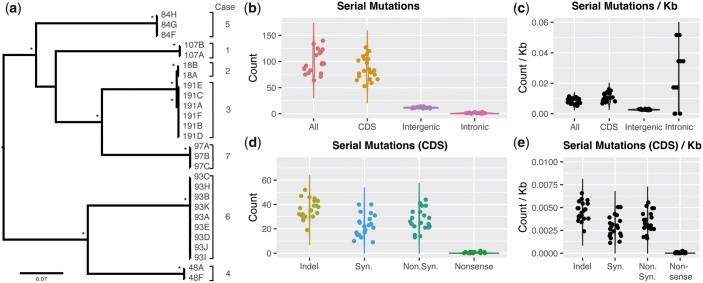
Fig. 6.
Microevolutionary changes across 7 sets of C. glabrata isolates. a) a RAxML phylogenetic tree of the serial isolates using the general-time-reversible model and CAT rate approximation with 100 bootstrap support. Branch lengths indicate the mean number of changes per site. b) The number of serial mutations total (All), those within protein-coding sequence (CDS), intergenic and intronic regions. c) Those same serial mutations per kb [calculated as the count of serial mutations divided by the total length of the feature (where All = whole genome) and multiplied by 1,000]. d) Serial mutations within CDS categorized by their effect on the sequencing: Insertion/Deletion (Indel), synonymous mutation (Syn.), nonsynoynmous mutation (Non.Syn.), and nonsense mutation. e) Those same serial mutations within CDS per kb.