Fig. 1.
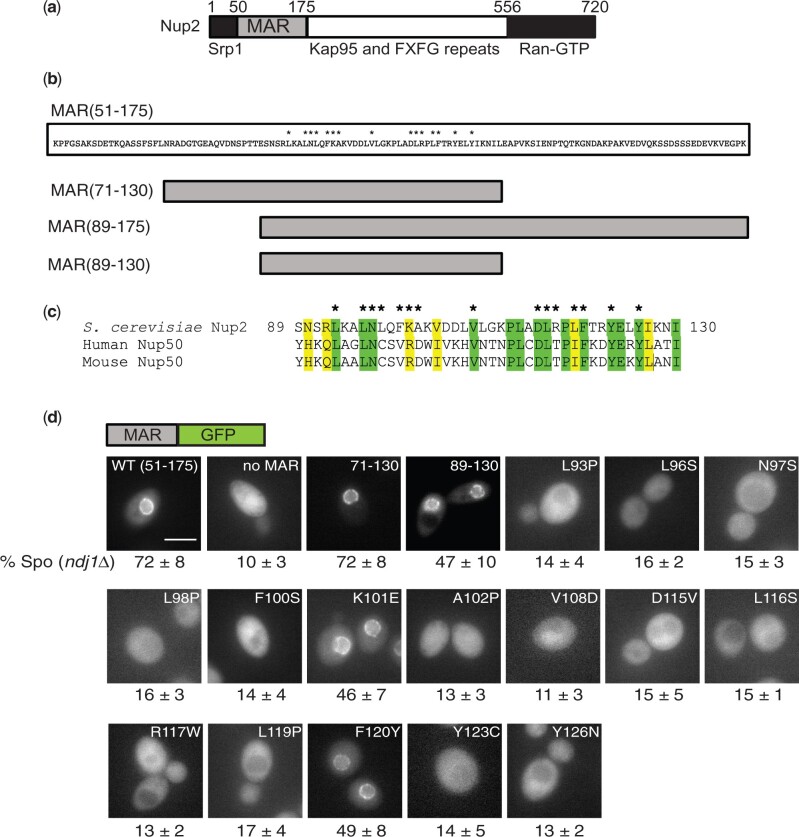
Location of point mutations in the Nup2 MAR and their effect on localization to the nuclear envelope. a) Schematic of the Nup2 protein showing the MAR (amino acid residues 51–175) and regions of Nup2 known to bind the transport proteins Srp1, Kap95 (importin-β), and Ran. b) Above: Amino acid sequence of the MAR, with asterisks indicating the positions of point mutations that affect MAR function. Below: Schematic depiction of deletion mutants of the MAR. c) Alignment of the functional region of the MAR with homologous regions in human and mouse Nup50. Similar and identical amino acids are highlighted. Asterisks indicate positions of the MAR point mutations. d) Images of cells expressing wild-type or mutant versions of the MAR fused to GFP. Above the panels is a schematic of the MAR-GFP fusion present in the strains. The label at the top of each panel indicates which version of the MAR is fused to GFP. The numbers below the panels are taken from Table 1 and are the sporulation efficiencies of strains carrying the depicted MAR-GFP fusions in an ndj1 background. The scale bar in the MAR(51–175)-GFP panel represents 5 µm. At least 20 individual cells were examined for each strain; in all cases, all cells had a similar appearance. Not all images were taken on the same day.