Table 2.
Ranking Metrics Used to Obtain a Treatment Hierarchy in Network Meta-Analysis, Their Formulas, and the Treatment Hierarchy Questions They Can Answer
| Ranking Metric | Method of Calculation | Treatment Hierarchy Question(s) |
|---|---|---|
Point estimate of the mean absolute estimand or relative treatment effect (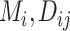 ) ) |
The center of the distribution of the absolute estimand or relative treatment effect | Which treatment has the smallest estimated mean value on the studied outcome? Which treatment has the largest estimated mean advantage compared with all other competitors? |
Probability of a treatment’s having the best mean outcome value (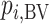 ) ) |
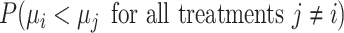
|
Which treatment is most likely to have the best (most desirable) mean value on the studied outcome? |
SUCRA for treatment i (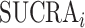 ) ) |
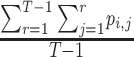 a
a
|
Which treatment has the largest fraction of competitors that it beats?b |
Mean rank (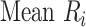 ) ) |
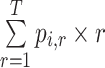 c
c
|
In the distribution of treatment effect ranks, which treatment has the largest mean rank? |
Median rank (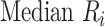 ) ) |
The value satisfying 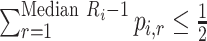 and and 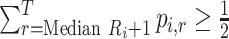
|
In the distribution of treatment effect ranks, which treatment has the largest median rank? |
Abbreviations: BV, best value; SUCRA, surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
a 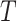 represents the number of competing treatments.
represents the number of competing treatments.
b Assuming a harmful outcome, we consider that a treatment 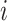 “beats” treatment
“beats” treatment 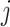 when the true mean values of the outcome fulfill
when the true mean values of the outcome fulfill 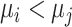 .
.
c 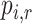 represents the probability that treatment i will produce the rth most favorable value (or will “beat” exactly r treatments).
represents the probability that treatment i will produce the rth most favorable value (or will “beat” exactly r treatments).
