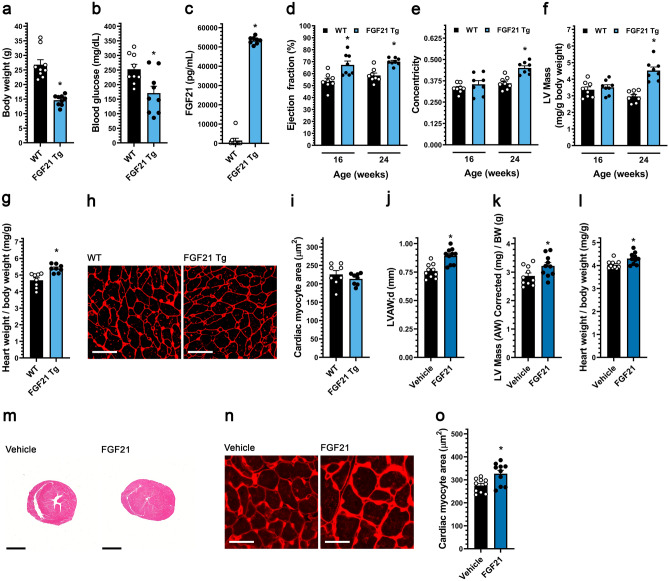
Figure 1.
Systemic FGF21 elevation in mice induces concentric cardiac hypertrophy. (a–i) Analysis of FGF21 transgenic (Tg) mice and wild-type littermates at 24 weeks of age unless otherwise indicated. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose levels, and (c) serum FGF21 levels. (d) Ejection fraction, (e) concentricity [relative wall thickness = (LVAW;d + LVPW;d)/LVID;d], and (f) left ventricular (LV) mass, as determined by echocardiography at 16 and 24 weeks of age. (g) Heart weight/body weight ratio, (h, i) wheat germ agglutinin staining of LV tissue (scale bar = 25 µm) and cardiac myocyte cross-section area. (j–o) Wildtype mice were injected i.v. with FGF21 or vehicle for five consecutive days before analysis on the 6th day. (j) LV anterior wall thickness (diastole), and (k) LV mass/body weight ratio, as determined by echocardiography. (l) Gravimetric heart weight/body weight ratio. (m) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained transverse heart sections (scale bar = 2 mm). (n, o) Wheat germ agglutinin staining of LV tissue (scale bar = 25 µm) and cardiac myocyte cross-section area. Statistical significance was determined by 2-way ANOVA with post-hoc testing with Sidak's multiple comparisons test (d–f), or by two-tailed t-test. All values are expressed as mean ± SEM. (a, b) N = 9; (c) N = 8–9; (d–f) N = 8, *p ≤ 0.05 vs. WT of same age; (g, i) N = 8, *p ≤ 0.05 vs. WT; (j–l, o), N = 10, *p ≤ 0.05 vs. vehicle. For the complete set of echocardiography parameters see Supplementary Tables 1 and 3.