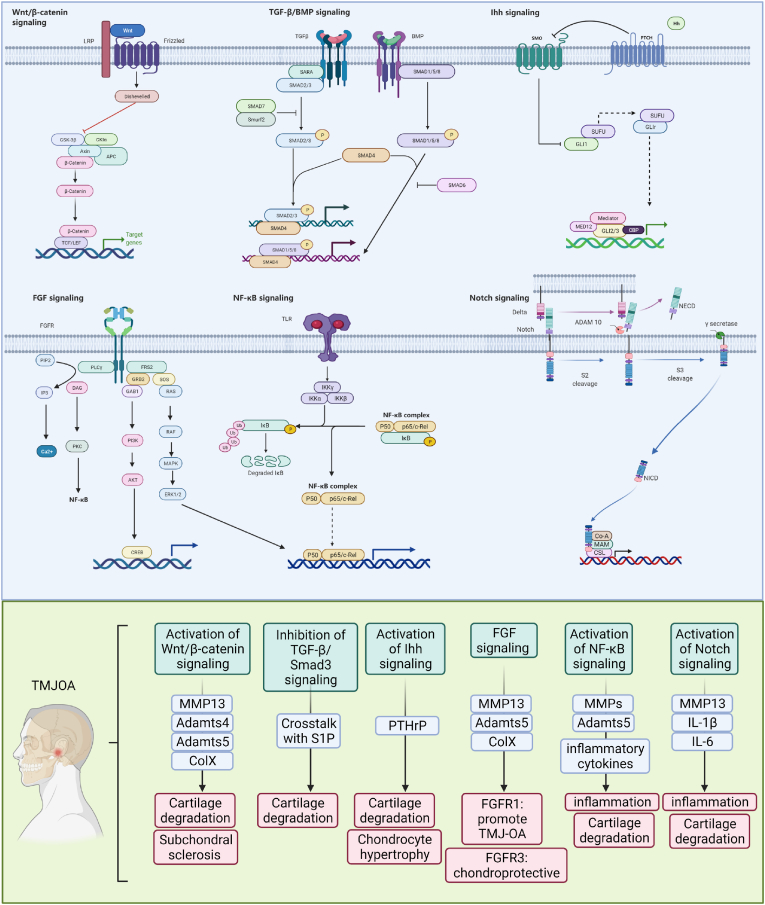
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of multiple signaling pathways in TMJ OA chondrocytes. Alterations of Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β, Ihh, FGF, NF-κB, and Notch signaling pathways lead to increased expression of matrix degrading proteases, including MMPs and Adamts4/5, promoting cartilage degradation. The activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling also affect subchondral bone of TMJ. The activation of Ihh pathway affects chondrocyte differentiation and maturation through PTHrP. The activation of NF-κB, and Notch pathways induces inflammation and accelerates TMJ OA development.