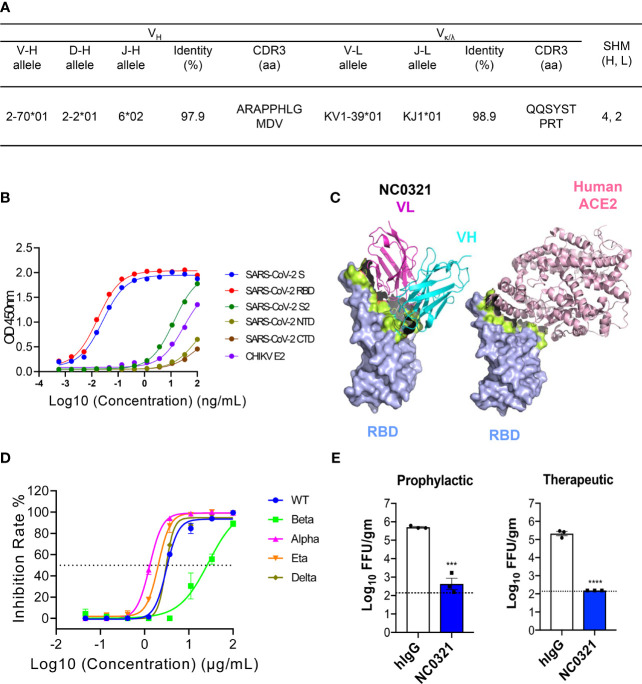
Figure 1.
Isolation of the potent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) human neutralizing antibody NC0321. (A) Germline analysis of the mAb NC0321. V-(D)-J rearrangement summary for the isolated mAb NC0321. (B) NC0321 isolated from a COVID-19 convalescent patient was tested for binding to SARS-CoV-2 spike (S), S1, S2, receptor-binding domain (RBD), N-terminal domain NTD, C-terminal domain CTD, and Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) E2 (as control) proteins in ELISA. (C) Computational models of SARS-CoV-2 RBD in complex with monoclonal antibody NC0312. Heavy (VH in cyan) and light (VL in purple) chains were colored as in (B), and the structures of the complex between hACE2 and RBD were provided as a comparison. Residues that contribute substantially to interactions are colored in green. (D) Neutralization activity of mAb NC0321 against multiple live SARS-CoV-2 variants (wild type, alpha, beta, delta, and eta) in Vero E6 cells. (E) Passive transfer of NC0321 confers protection to mice prophylactically and therapeutically; we transferred 10 mg/kg NC0321 (200 µl in PBS) into Ad5-hACE2-transduced mice (6–8 weeks) intraperitoneally 1 day before or 1 day after the intranasal (I.N.) infection with 1 × 105 FFU SARS-CoV-2 strain (SARS-CoV-2/human/CHN/IQTC01/2020, GenBank: MT123290.1). Virus titers in the lungs were measured at 3 dpi. **** indicate p-values of <0.0001, *** p-values of 0.0001<p<0.001.