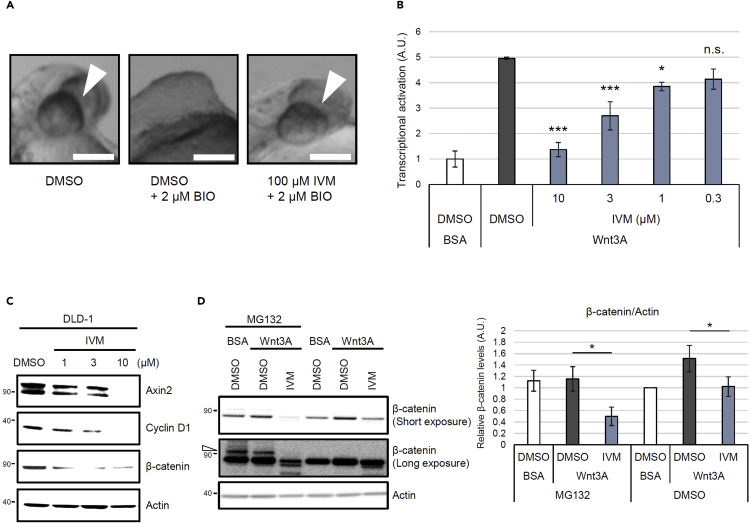
Figure 1.
Ivermectin (IVM) suppresses the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in zebrafish embryos and mammalian cells
(A) IVM was identified as a chemical suppressor of the eyeless phenotype. Zebrafish embryos were pretreated with 100 μM IVM at 50% epiboly. They were then treated with 6-bromo-indirubin-3′-oxime (BIO), which is a GSK3 inhibitor that leads to the accumulation of β-catenin, at the shield stage and were incubated for 24 h. Images were obtained at 30 h postfertilization. Scale bar = 200 μm. See also Figure S1.
(B) IVM reduced the β-catenin/TCF-dependent transcriptional activity. Human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells were transiently cotransfected with Super 8x TOPFlash—a firefly luciferase reporter plasmid—to monitor the β-catenin/TCF-dependent transcriptional activity and with pRL-SV40—a renilla luciferase reporter plasmid—to normalize the transfection efficiency. The cells were pretreated with IVM at the indicated concentrations for 1 h and then treated with 50 ng/mL of Wnt3A for 18 h in 1% fetal bovine serum (FBS)–supplemented Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM). Transcriptional activation in the cells was assayed by measuring the firefly and renilla luciferase activities. Normalized relative luciferase activities were calculated by dividing firefly luciferase activities by those of renilla. Transcriptional activation levels are indicated as values relative to the control (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]-treated and bovine serum albumin [BSA]–treated cells). Data are presented as the means ± standard errors of the means (n = 4 biological replicates). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, n.s.: not significant, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test.
(C) IVM downregulated the target proteins involved in Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Human colorectal cancer DLD-1 cells were treated with IVM at the indicated concentrations for 18 h in 1% FBS-supplemented RPMI 1640 medium. Subsequently, the cytoplasmic fractions of the cells were probed for Axin2, cyclin D1, β-catenin, and actin.
(D) IVM reduced the cytoplasmic β-catenin levels in the presence of a proteasomal inhibitor, MG132. HEK293 cells were first treated with 25 μM MG132 for 15 min, followed by treatment with 10 μM IVM for 1 h and 50 ng/mL of Wnt3A for 2 h in 1% FBS/DMEM. The cytoplasmic proteins were probed with anti-β-catenin and anti-actin antibodies (the left panel). The band intensities were quantified, normalized to the actin levels, and reported as values relative to the control (DMSO-treated and BSA-treated cells in the absence of MG132; right panel). The open triangle indicates the bands of ubiquitinated β-catenin. Data are presented as the means ± standard deviations (SDs; n = 3 biological replicates). ∗p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. See also .Figure S2