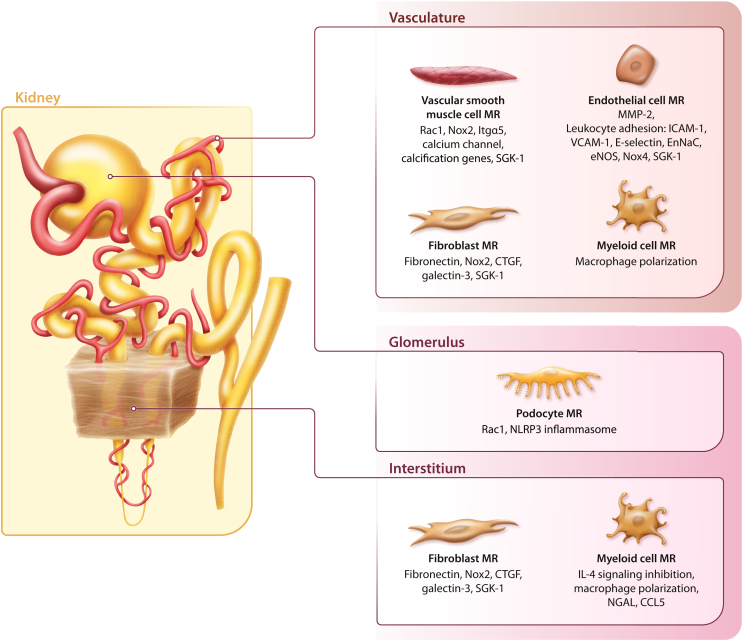
Figure 1.
Potential mediators of cellular injury following mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) overactivation in nonepithelial cells, leading to vascular dysfunction, inflammation, and fibrosis. CCL5, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; EnNaC, epithelial sodium channel in the endothelium; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL-4, interleukin-4; Itgα5, integrin subunit α 5; MMP-2, matrix metalloproteinase-2; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain–like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing 3; NOX, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase; Rac1, Rac family small GTPase 1; SGK-1, serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.