Figure 5.
D14 degradation after GR245DS treatment is enhanced by SMAX1 and SMXL2.
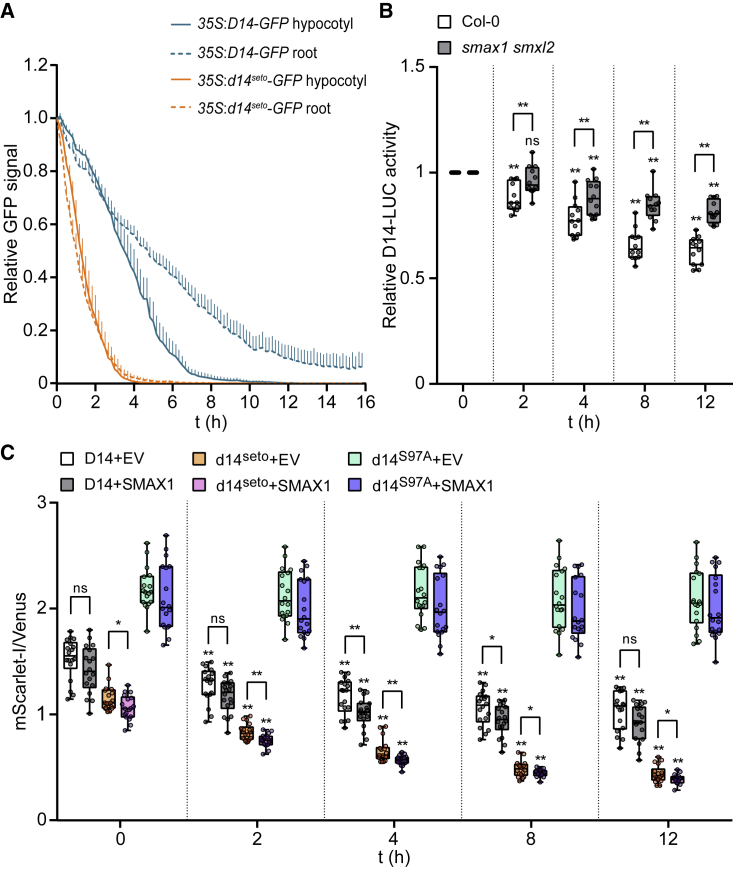
(A) The relative GFP signal from D14-GFP or d14seto-GFP transgenic plants was measured every 10 min in the presence of 5 μM rac-GR24. The curve was generated from the mean value per genotype/treatment at each time point. Bar indicates SE of the mean (n = 6 seedlings).
(B)UBQ:D14-LUC transgenic seedlings in the Col-0 and smax1 smxl2 backgrounds were treated with 5 μM GR245DS or acetone for 12 h. Bioluminescence is shown as relative LUC activity at 0, 2, 4, 8, and 12 h after treatment. n = 10–12 seedlings. Asterisks indicate significant differences relative to each group at 0 h or between compared pairs using Student's t test (∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01; ns, no significance).
(C) Time-course assay of D14, d14seto, and d14S97A stability in N. benthamiana under 10 μM GR245DS treatment. Relative fluorescence from the D14-mScarlet-I reporter, the d14seto-mScarlet-I reporter, or the d14S97A-mScarlet-I reporter and the Venus reference after transient co-expression of the ratiometric system and SMAX1 effector in tobacco is shown. Leaf discs were treated for 12 h to monitor D14, d14seto, and d14S97A stability. n = 14 leaf discs. Asterisks indicate significant differences relative to each group at 0 h or between compared pairs using Student's t test (∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01; ns, no significance).