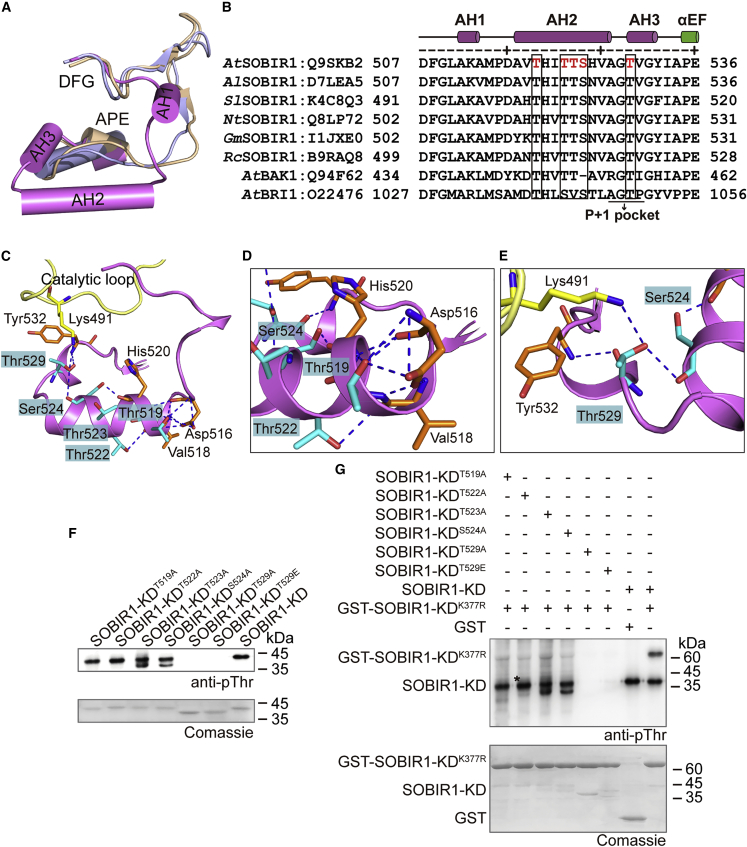
Figure 3.
Analyses of the phosphorylation sites in the activation segment of SOBIR1-KD
(A) Comparison between the SOBIR1-KD activation segment and the BRI1 and BAK1 structures. SOBIR1, BRI1, and BAK1 are presented in magenta, beige, and light blue, respectively.
(B) Sequence alignment of the activation segments of SOBIR1 orthologs from different species as well as AtBAK1 and AtBRI1. The Swiss-Prot ID is provided after each protein name. The secondary structure elements of SOBIR1-KD are indicated above the sequences. Phosphorylation sites identified in AtSOBIR1-KD are highlighted in red. Conserved phosphorylation sites in the kinases are indicated in a black box. The P+1 pocket is labeled accordingly. At, A. thaliana; Al, Arabidopsis lyrata; Sl, S. lycopersicum; Nt, Nicotiana tabacum; Gm, Glycine max; Rc, Ricinus communis.
(C–E) View of the interaction networks of Thr519, Thr522, Ser524, and Thr529 in the SOBIR1-KD activation segment. The activation segment is presented in magenta, whereas the catalytic loop is in yellow. The phosphorylation sites identified by LC-MS/MS are labeled and presented in cyan, and the interacting residues are highlighted in orange (in the activation segment) or yellow (in the catalytic loop). Hydrogen bonds are presented as blue dashed lines. Detailed interactions of Thr519, Thr522, Ser524 (D), and Thr529 (E) are presented.
(F) Phosphorylation states of the activation segments of the SOBIR1-KD mutants.
(G) Western blot analysis of the transphosphorylation of SOBIR1-KDK377R by the SOBIR1-KD mutants. The reaction mixture contained 10 μM GST-SOBIR1-KDK377R and 1 μM SOBIR1-KD mutants. As a negative control, GST was incubated with wild-type SOBIR1-KD, and its phosphorylation signal was undetectable. All proteins in this assay were recombinantly expressed in E. coli. Asterisk (∗) represents a nonspecific band.