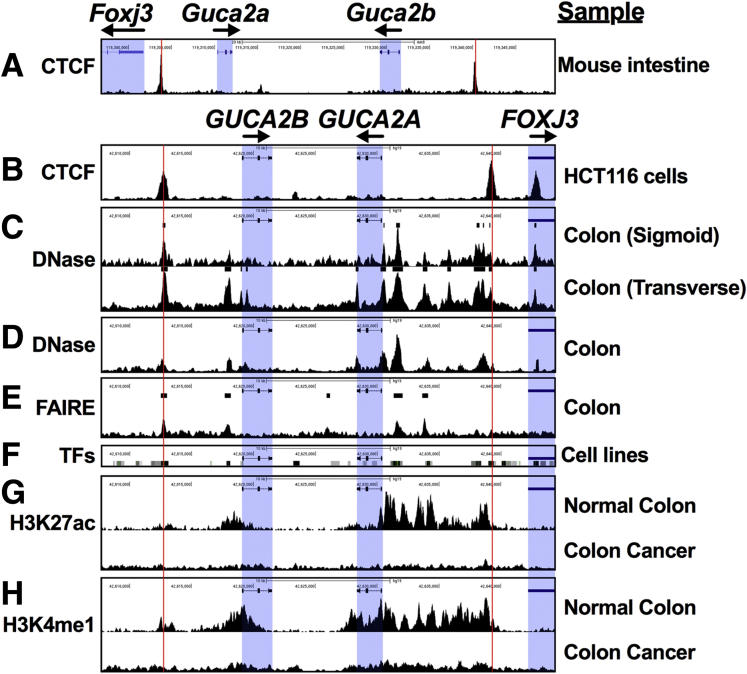
Figure 4.
Regulatory elements in the GUCA locus are silenced in colorectal cancer. Public datasets reveal regulatory features in the GUCA2A locus. (A) CTCF ChIP-seq from mouse intestinal epithelial cells (GSE98724; mm9, chr4:119,296,885–119,349,526). (B) CTCF ChIP-seq from human HCT116 colon cancer cells (GSE92879; hg19, chr1:42,607,745–42,644,356). (C) DNase-seq from sigmoid (top; GSE90366) and transverse colon (bottom; GSE90398). (D) DNase-seq from normal colon crypts (GSE77737). (E) Formaldehyde-assisted identification of regulatory elements (FAIRE) sequencing from normal colon (GSE94935). (F) Clusters of transcription factor density, representing ChIP-seq of 338 factors in 130 cell types (UCSC Genome Browser, ENCODE Transcription Factor Binding track). (G) H3K27ac ChIP-seq and (H) H3K4me1 ChIP-seq identified poised enhancers in normal colon (top) but not in colon cancer (bottom) (GSE77737). Red lines denote CTCF binding sites. Blue boxes denote gene bodies. Sequencing datasets were obtained from NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus and visualized in the UCSC genome browser.