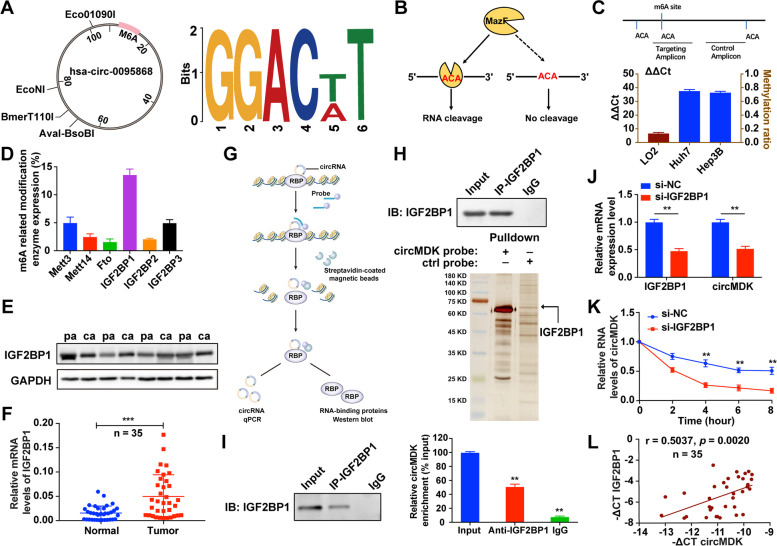
Fig. 3.
IGF2BP1 identifies m6A modified circMDK and improves the transcript stability of circMDK. A Bioinformatics analysis showed that there were m6A modification sites in circMDK. B The schematic diagram of MazF-PCR restriction endonuclease digestion. C The abundance of m6A modified circMDK in cells was detected by MazF-PCR. D The expression level of methylation-related proteins was verified by qRT-PCR. E The protein levels of IGF2BP1 in four paired HCC samples. pa: para-carcinoma tissues; ca: cancer tissues. F The qRT-PCR analysis of IGF2BP1 in 35 paired HCC samples. ***p < 0.001. G The schematic diagram of RIP assay. H Identification of the circMDK-protein complex pulled down by circMDK junction probe with protein extracts from Hep3B cells. The arrow indicates IGF2BP1. I RIP assays showing the association of IGF2BP1 with circMDK. Left, IP efficiency of IGF2BP1-antibody shown in western blotting. Right, relative enrichment representing RNA levels associated with IGF2BP1 relative to an input control. IgG antibody served as a control. **p < 0.01. J Transcript levels of IGF2BP1 and circMDK in negative control and si-IGF2BP1 HCC cells. **p < 0.01. K Reduction of circMDK RNA stability in IGF2BP1 knockdown HCC cells as compared with control. Cells were treated with Actinomycin D at the indicated time points. Error bars indicate SD. The t test was applied to analyze the statistical significance between two groups. **p < 0.01. L Correlation analysis revealed positive correlation between the levels of circMDK and IGF2BP1 mRNA in the tumorous tissues of the 35 HCC patients. Data are shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments