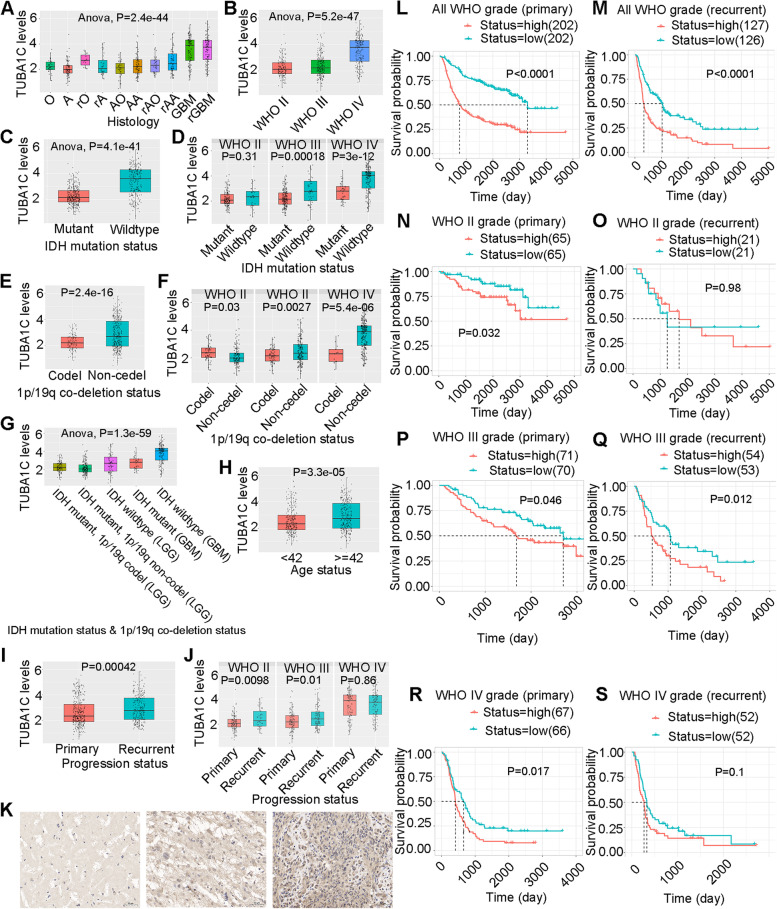
Fig. 14.
Expression levels of TUBA1C in glioma and normal tissues. TUBA1C expression in gliomas of different histology (A) and different WHO subtypes (B). TUBA1C expression in patients with different IDH mutation statuses (C) and different WHO subtypes (D). TUBA1C expression in patients with different 1p/19q codeletion statuses (E) and different WHO subtypes (F). TUBA1C expression in patients with different IDH mutation statuses and 1p/19q codeletion statuses (G) and different ages (H). TUBA1C expression in patients with different progression statuses (I) and different WHO subtypes (J). K TUBA1C expression in normal (left), low-grade glioma (middle) and high-grade glioma (right) tissue. Scale bars = 50 μm. Survival probability in the groups with different TUBA1C expression levels in all WHO subtypes of primary glioma (L) and recurrent glioma (M). Survival probability in the groups with different TUBA1C expression levels in WHO grade II primary glioma (N) and recurrent glioma (O). Survival probability in the groups with different TUBA1C expression levels in WHO grade III primary glioma (P) and recurrent glioma (Q). Survival probability in the groups with different TUBA1C expression levels in WHO grade IV primary glioma (R) and recurrent glioma (S)