Figure 7. Nanochannel-based technology to modulate the direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced endothelial cells as therapeutic agents for stroke.
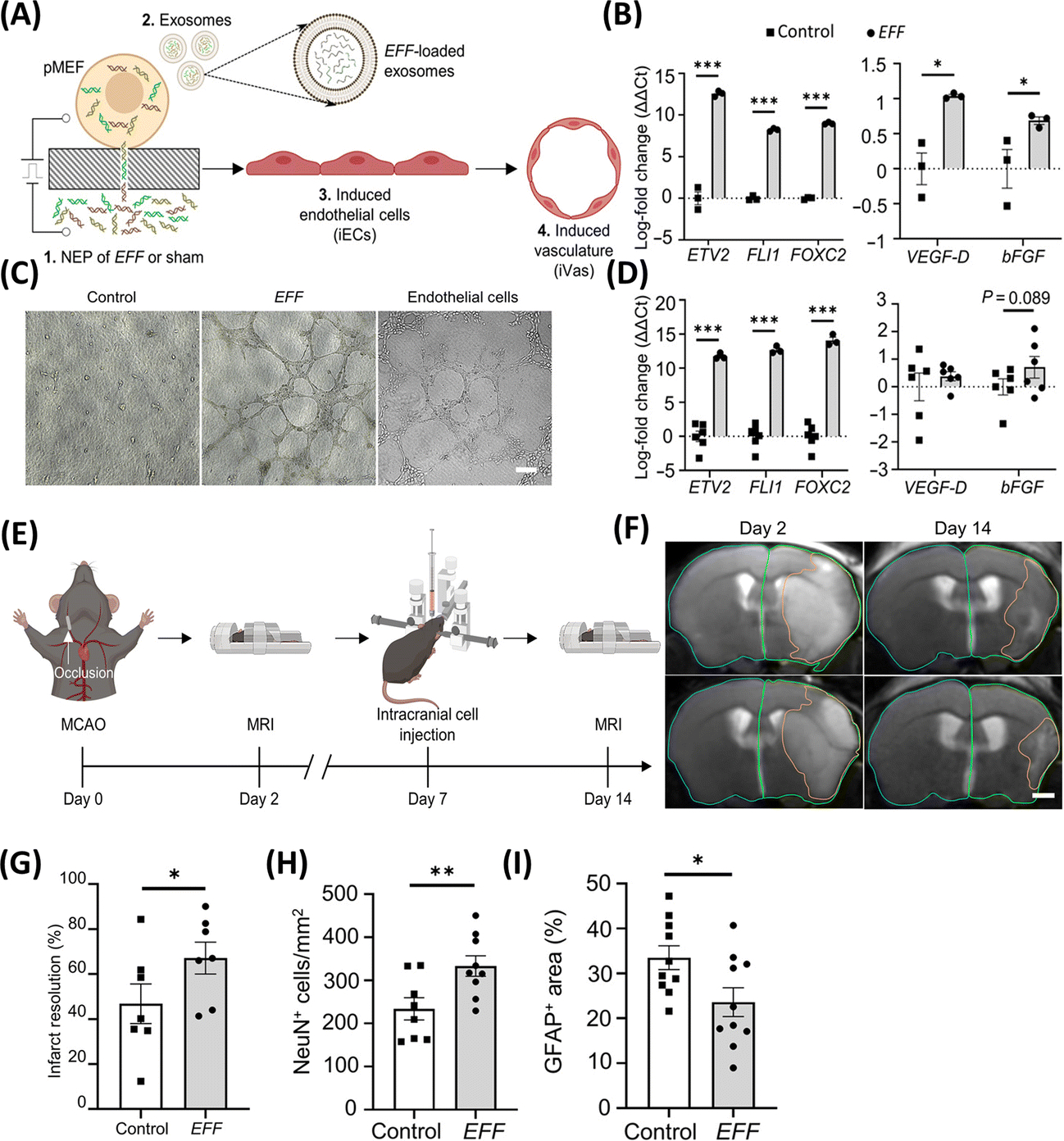
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating the nanotransfection with EFF, release of pro-vasculogenic/angiogenic EVs (e.g., exosomes), and reprogramming of fibroblasts into induced endothelial cells (iECs) that subsequently mediate the formation of induced vasculature (iVas). (B) Upregulation of genes in nanotransfected cells and (C) loaded in released exosomes. (D) In vitro tube formation assay in the EFF group. (E) Schematic diagram of middle cerebral artery occlusion, intracranial injection, and MRIs. (F, G) T2-weighted MR images post-stroke show that intracranial injection of EFF-nanotransfected cells led to significantly improved infarct resolution compared to control in mice that exceeded 17% weight loss. EFF-nanotransfected cells injected in mice show (H) superior neuronal cellularity (NeuN) and (I) reduced astroglial scar formation (GFAP) (Adapted from Lemmerman et al., 2021. Ref 68).
