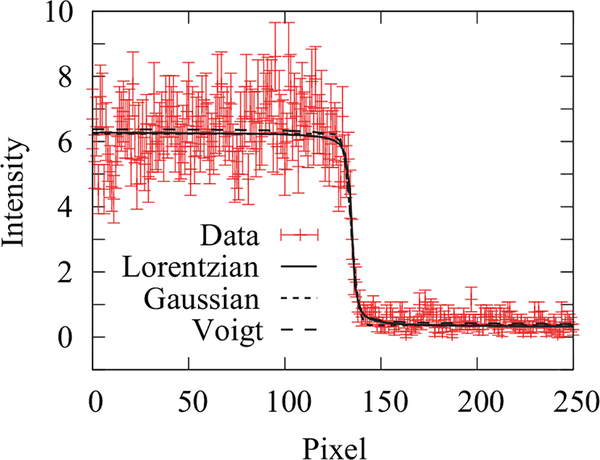
FIG. 2.
(a) The line profile across a sharp Gd edge. Three system PSFs (a Lorentzian, a Gaussian, and a Voigt profile) are used to model the measured line profile, and all three models result in a reduced χ2 ≈ 1. In the case of the Lorentzian model, the obtained half width at half maximum is γ = (6.0 ± 1.5) μm, corresponding to a resolution of 8.2 μm with a reduced χ2 = 0.94. In the case of the Gaussian model, the obtained σ = (14.9 ± 2.1) μm, corresponding to a resolution of 21.8 μm with a reduced χ2 = 0.98. In the case of the Voigt model, the obtained σ = (9.0 ± 0.4) μm and γ = (4.0 ± 0.4) μm, corresponding to a resolution of 21.8 μm with a reduced χ2 = 1.02. The uncertainty in the neutron counts is assumed to be from random noise, reduced by averaging over 8 pixels.