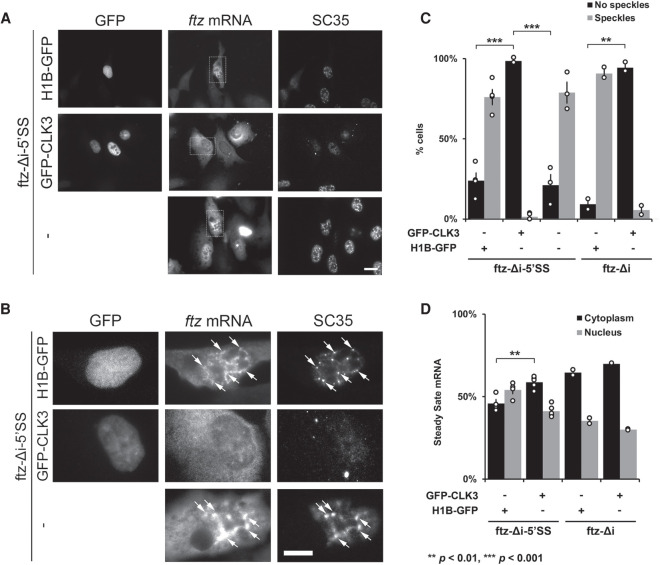
FIGURE 5.
Nuclear speckles promote mRNA nuclear retention of 5′SS motif containing mRNA. (A–D) U2OS cells were cotransfected with either ftz-Δi-5′SS or ftz-Δi, and with either H1B-GFP, GFP-CLK3, or empty vector (“-”). Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cells were fixed and stained for ftz mRNA by FISH and for the speckle marker SC35 by immunofluorescence. Representative images, with each row depicting a single field of view imaged for GFP, ftz mRNA, and SC35 is shown in A. Scale bar, 10 µM. Enlarged images of the regions indicated in A are depicted in B. Examples of ftz/SC35 colocalization are indicated with arrows. Scale bar, 10 µM. Note that the overexpression of GFP-CLK3 disrupts nuclear speckles (SC35) compared to H1B-GFP or non-GFP-expressing cells. (C) The number of cells that lacked or contained nuclear speckles were quantified. Each bar represents the average and standard error of two (ftz-Δi) or four (ftz-Δi-5′SS) independent experiments, each consisting of 30–50 cells. Note that expression of GFP-CLK3 disrupts nuclear speckles compared to control cells. (**) P < 0.01, (***) P < 0.001 (Student's t-test). (D) Quantification of the cytoplasmic/nuclear FISH signal with each bar representing the average and standard error of two (ftz-Δi) or four (ftz-Δi-5′SS) independent experiments, each experiment consisting of at least 30 to 60 cells. (**) P < 0.01 (Student's t-test).