Figure 1: SULF2 Expression is Increased in Many Human Cancers, Including Cholangiocarcinomas, at mRNA and Protein Levels.
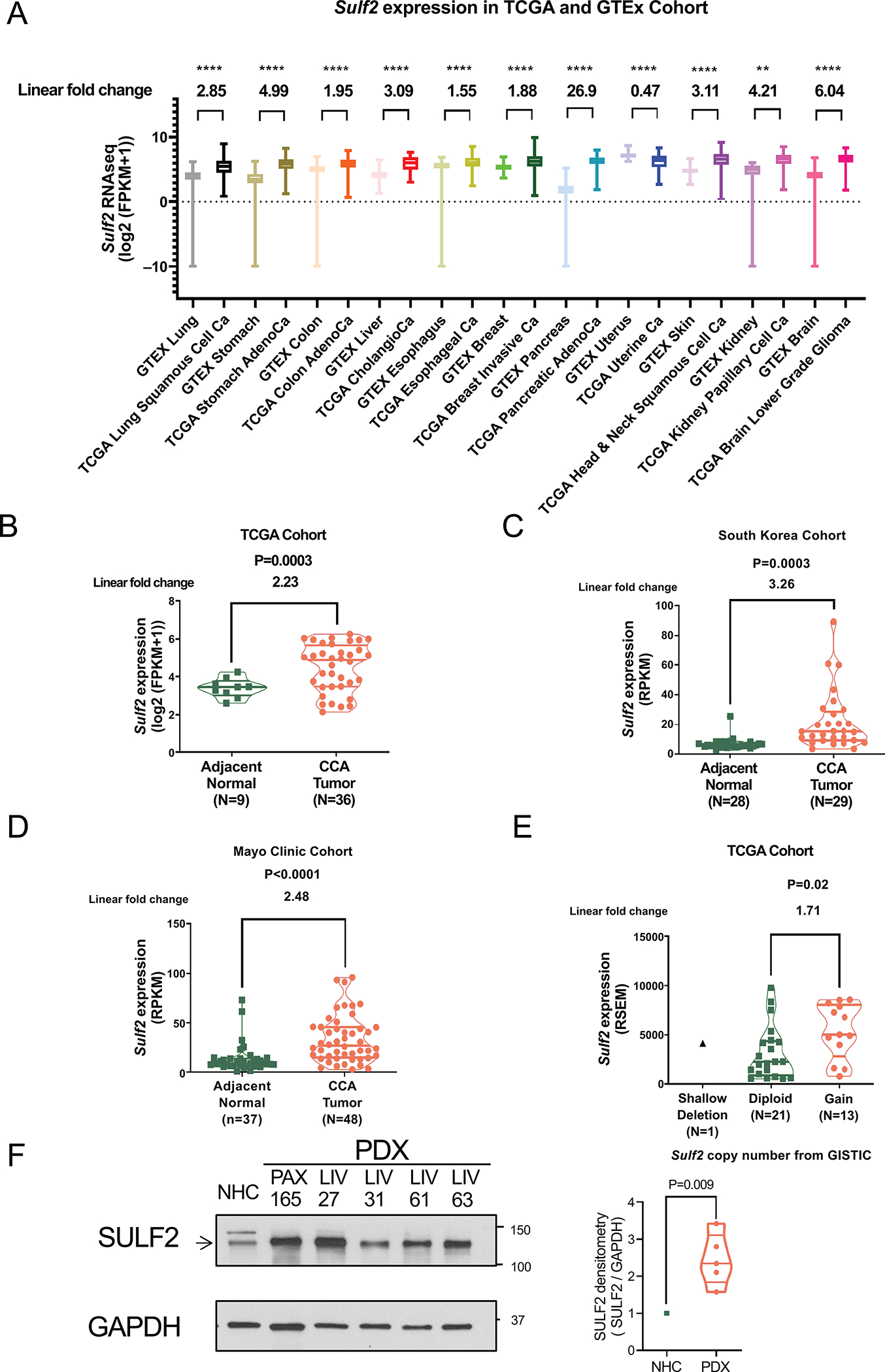
(A) In silico analysis of SULF2 expression in human normal tissue from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) program cancer samples. SULF2 gene expression is in units of log2(FPKM+1). (B) In the TCGA dataset, SULF2 gene expression in CCA is compared to expression in adjacent normal tissue. Gene expression is in units of log2(FPKM+1). (C) In a South Korean RNA sequence dataset, SULF2 gene expression in CCA is compared to adjacent normal tissue. SULF2 gene expression is in units of RPKM. (D) In a Mayo Clinic RNA sequence dataset, SULF2 gene expression in CCA is compared to adjacent normal tissue. SULF2 gene expression is in units of RPKM. (E) Of the TCGA CCA samples, 13 out of 35 CCAs (37.1%) show gain of SULF2 copy number, which is associated with a significantly higher SULF2 mRNA expression level than is seen in diploid CCAs (F) Western immunoblotting shows that five CCA PDXs express high levels of SULF2 protein compared to normal human cholangiocytes (NHC). **: p<0.01, ****: p<0.0001.
