Figure 4. Sex differences in endothelin‐1 signaling pathway activation in the inner medulla under NS conditions.
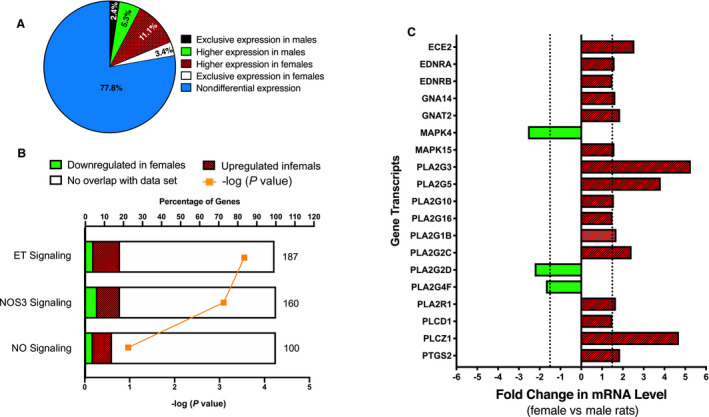
Inner medullae were collected from NS‐fed Sprague Dawley rats (n=8/sex) and pooled (n=4 rats/pool/group) by sex for RNA sequencing analysis and subsequent IPA. Graphical representation of the sex differences in the renal inner medullary transcriptome (A). Graphical representation of the sex differences in transcript expression found within enriched IPA pathways with established roles in natriuresis (ET signaling, NOS3 signaling, and NO signaling in the cardiovascular system) (B). Pathways are ranked by –log (P value). The total number of genes found within each pathway is shown on the right of the respective bar. Graphical represenation of the relative abundance of inner medullary gene transcripts involved in the endothelin‐1 natriuretic signaling pathway in male and female rats (C). Gene transcripts that were differentially expressed and/or altered by at least 1.5‐fold in female rats relative to males are shown. IPA indicates Ingenuity Pathway Analysis; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; and NS, normal salt.
