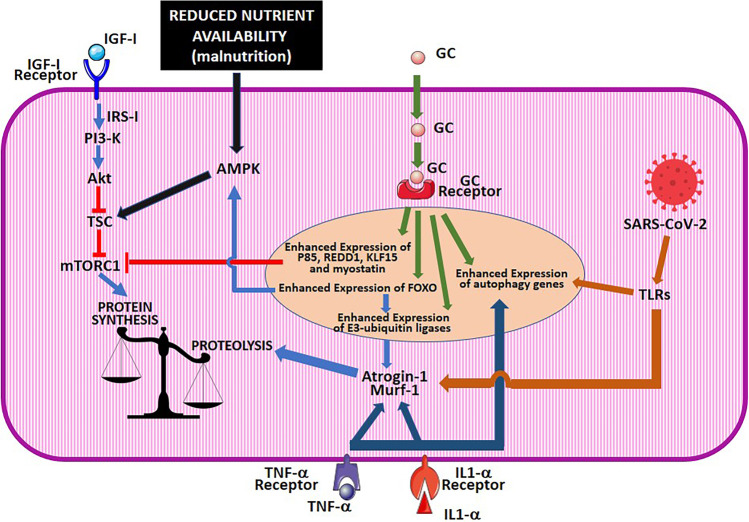
Fig. 1.
Molecular mechanism of muscle damage in CoVID-19. The drawing schematically illustrates how, in CoVID-19, muscle damage is produced by different but converging factors, which include malnutrition, cytokine receptor activation, and the activation of glucocorticoid receptors either by exogenous glucocorticoid drugs, given to treat this disease, or by endogenous glucocorticoid hormones, released in response to stress. The figure was prepared using the clip arts freely available under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License at the Servier Medical Art (SMART) website (https://smart.servier.com/). IGF, insulin-like growth factor; GC, glucocorticoids; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex; mTORC, mechanistic Target of Rapamycim complex; AMPK, 5′-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; REDD1, regulated in development and DNA damage responses 1; KLF, Krüppel-like factor; FoxO, forkhead box O; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; TLRs, Toll-like receptors; IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha