Figure 2. Summary of the key findings of the meta‐analysis.
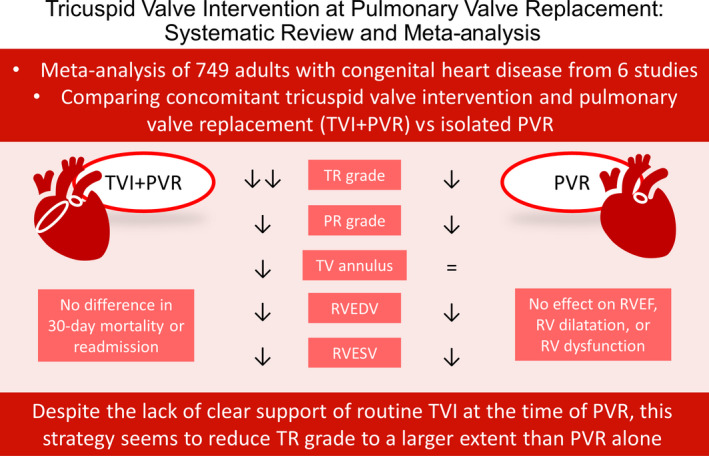
Both TVI+PVR and PVR reduced TR grade, PR grade, RVEDV, and RVESV. TVI+PVR, but not PVR, was associated with a decrease in TV annulus. Furthermore, TVI+PVR was associated with a larger decrease in TR grade compared with PVR. No evidence could be established for an effect of either treatment on RVEF or RV dilatation and RV dysfunction as qualitatively assessed by echocardiography of either treatment. There was no evidence for a difference in hospital mortality or reoperation for TR. PR indicates pulmonary regurgitation; PVR, pulmonary valve replacement; RV, right ventricular; RVEDV, right ventricular end‐diastolic volume; RVEF, right ventricular ejection fraction; RVESV, right ventricular end‐systolic volume; TR, tricuspid regurgitation; TV, tricuspid valve; and TVI, tricuspid valve intervention.
