Figure 2. Associations of depressive symptoms with incident heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), and the composite outcomes HFpEF/death and HFrEF/death.
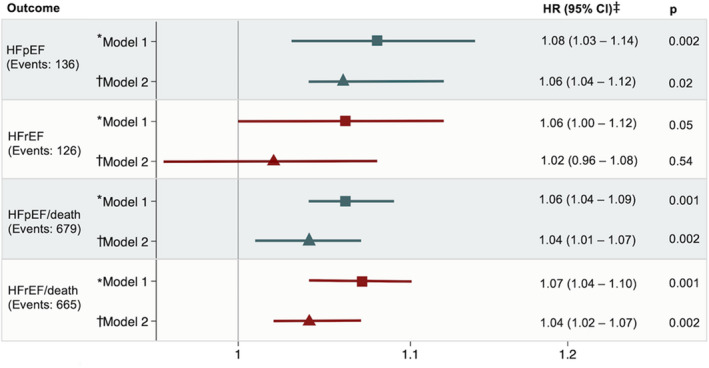
Greater depressive symptoms were associated with a higher risk of developing HFpEF but not HFrEF after adjusting for demographics and cardiovascular risk factors. *Model 1 adjusts for demographics (age, sex, and race). †Model 2 adjusts for model 1, socioeconomic indicators (education and income), health behaviors (smoking, drinking, and physical activity), and prevalent chronic conditions and cardiovascular risk factors (diabetes mellitus, body mass index, heart rate, and estimated glomerular filtration rate). ‡Hazard ratio (HR) is per unit increase in Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale score.
