Figure 3. Adjusted hazard ratio for the association between high SUA/SCr ratio (Q4) and risk of cardiovascular diseases stratified by (A) age, (B) kidney function status, and (C) glucose status subgroups.
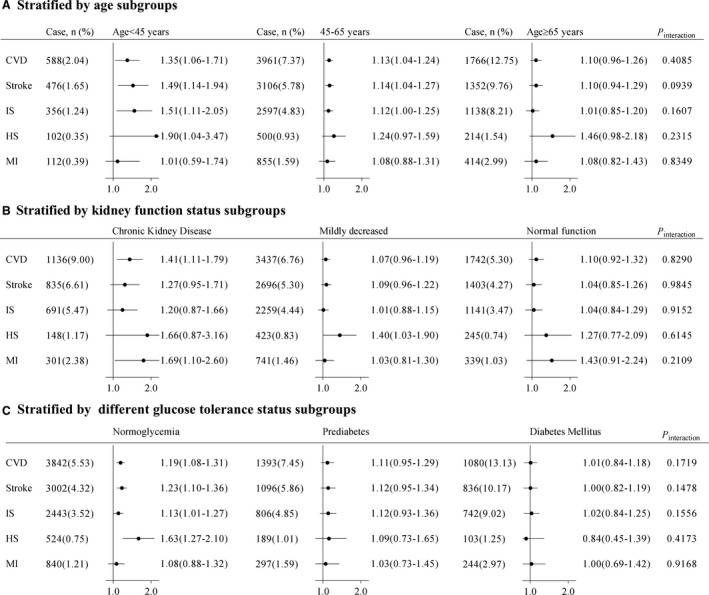
Adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, education, income, smoke, drink, physical activity, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, proteinuria, diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers treatment, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, and high sensitivity C‐reactive protein other than variables for stratification. Chronic kidney disease was defined as eGFR<60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, mild decrease was defined as eGFR ranged of 60 to 89 mL/min per 1.73 m2, normal function was defined as eGFR ≥90 mL/min per 1.73 m2. Normglycemia was defined as a fasting plasma glucose <5.6 mmol/L, prediabetes was defined as a fasting plasma glucose of 5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L, and diabetes mellitus was defined as a fasting plasma glucose ≥7.0 mmol/L, or in those taking oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin, or having a history of diabetes mellitus. CVD indicates cardiovascular disease; HS, hemorrhagic stroke; IS, ischemic stroke; MI, myocardial infarction; and SUA/SCr, serum uric acid to serum creatinine ratio.
