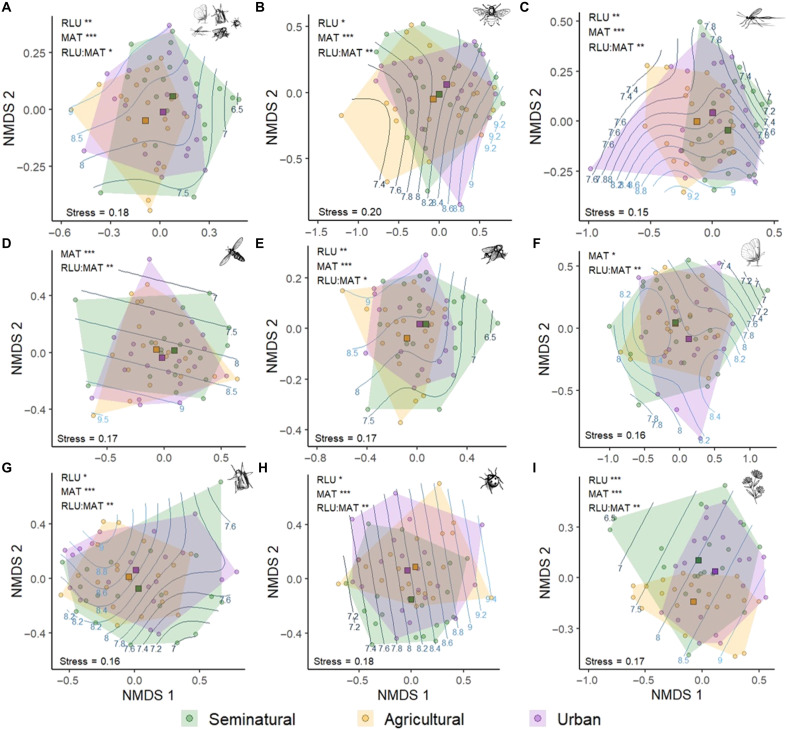
Fig. 2. Overlap in species composition among the three major regional land-use types (RLU) and their interaction with multiannual mean temperature (MAT).
Diagrams show ordinations based on NMDS of Jaccard’s dissimilarity matrices. The position of regions (dots, n = 60) in the NMDS space represents the similarity in pollinator community composition in relation to other regions: the closer the dots, the higher the proportion of species shared. Squares represent centroids of the three regional land-use types; polygons delimit the NMDS space occupied by regions with the same regional land-use type; and lines in the background represent contour lines of temperature. The different panels show (A) whole pollinator community, (B) bees, (C) non-bee Hymenoptera, (D) syrphids, (E) non-syrphid Diptera, (F) butterflies, (G) moths, (H) beetles, and (I) flowering plants. Significant effects of MAT, RLU, and their interaction based on permutational multivariate analysis of variance are shown in the top left corner of each panel (table S2). Significance levels: ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, and *P < 0.05.