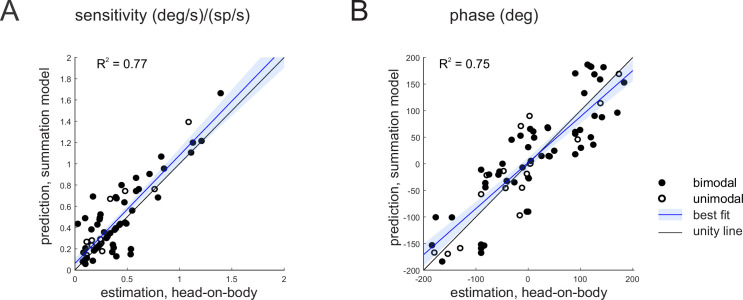
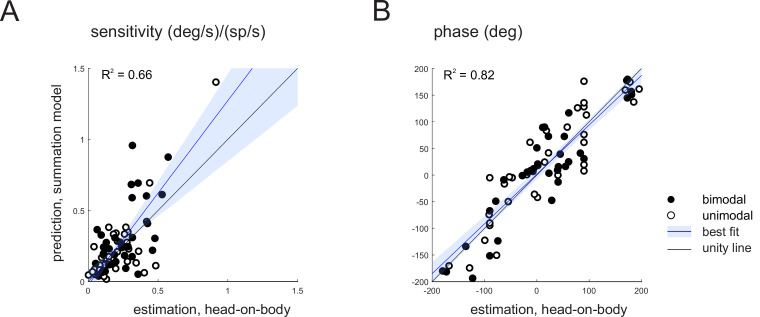
Figure 4. Purkinje cell simple spike’s responses to combined stimulation are well predicted by the linear summation of a given neuron’s responses to vestibular and proprioceptive stimulation when applied alone.
(A, B) Comparison of estimated and predicted sensitivities (A) and phases (B) of Purkinje cell’s responses to head-on-body rotations in the preferred movement direction. The linear summation of a given neuron’s vestibular and neck proprioceptive sensitivities well predicts both sensitivity and phase measures in the combined condition. Blue lines and shading denote the mean ± 95% CI of linear fit.