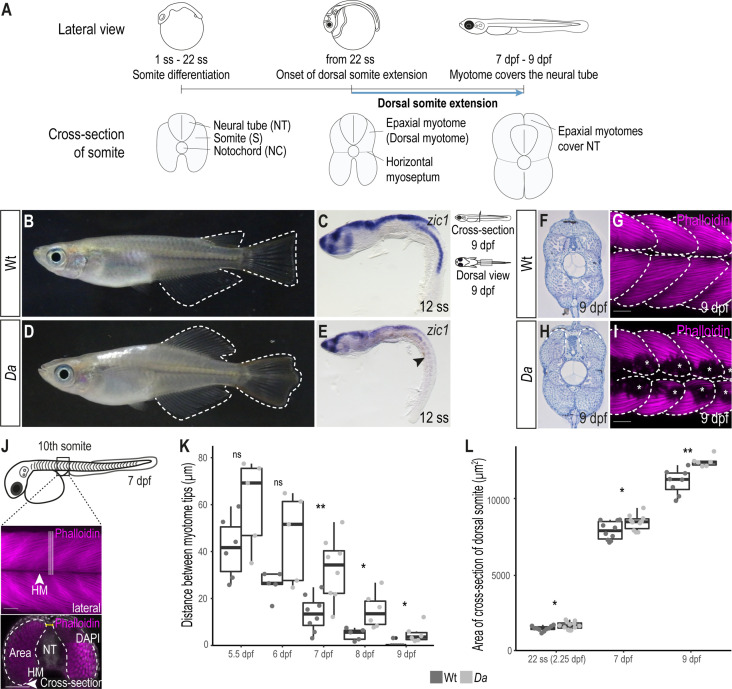
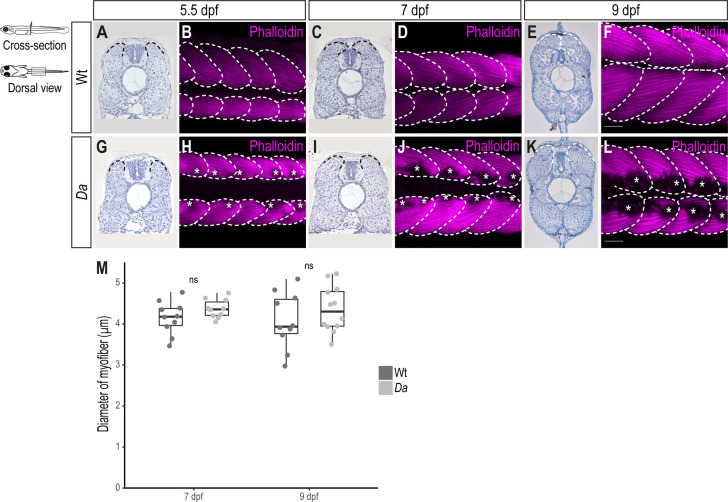
Figure 1. The epaxial myotome of the Da mutant fails to cover the neural tube at the end of embryonic development.
(A) Schematic representation of dorsal somite extension which results in the full coverage of the neural tube by the epaxial myotomes at the end of embryonic development. (B) Lateral view of adult Wt medaka. Dorsal, caudal, and anal fins are outlined. (C) Lateral view of whole-mount in situ hybridization against zic1 in a 12 ss (1.7 dpf, stage 23) Wt embryo. zic1 expression can be observed in the brain, neural tissues and the dorsal somites. (D) Lateral view of adult Da mutant. Dorsal, anal and caudal fins are outlined. The dorsal trunk region resembles the ventral trunk region. (E) Lateral view of whole-mount in situ hybridization against zic1 of a 12 ss Da embryo. zic1 expression can be observed in the brain and the neural tissues, but is drastically decreased in the dorsal somites (arrowhead). (F, H) Cross-sections of tail regions of hematoxylin stained 9 dpf embryos. Dorsal ends of myotomes are outlined. In Wt, the left and the right myotome come in close contact at the top of the neural tube and form a gapless muscle layer (F). In the Da mutant, the left and right myotome fail to come in contact at the top of the neural tube (H). (G, I) Dorsal view of whole-mount Phalloidin (magenta) immunostaining labeling the myotome of Wt (G) and Da (I) embryos. Epaxial myotome is outlined, and asterisks label melanophores. The contour of the myotomes was drawn based on the Z-stack images of the dorsal myotomes to avoid ambiguity caused by melanophores. Anterior to the left. (J) Schematic representation of measurements to analyze the distance between the left and the right dorsal tip of the myotome (yellow) and the cross-sectional area of the dorsal myotome. For each measurement, three consecutive optical cross sections of the 10th somite were analyzed and averaged. (K) Distance between the left and right tip of the dorsal myotome 5.5 dpf – 9 dpf (n = 6 and 5 for Wt and Da embryos, respectively at 5.5 dpf (stage 35) (p = 0.097); n = 5 and 5 at 6 dpf (stage 36) (p = 0.075); n = 8 and 8 at 7 dpf (stage 37) (p = 0.0047); n = 5 and 6 at 8 dpf (stage 38) (p = 0.019); n = 7 and 6 at 9 dpf (stage 39) (p = 0.034); median, first and third quartiles are shown). (L) Cross-sectional area of the dorsal somites at 22 ss (2.25 dpf, stage 26; n = 10 somites of 5 Wt embryos, n = 12 somites of 6 Da embryos) (p = 0.038), 7 dpf (n = 10 somites of 5 Wt embryos, n = 10 somites of 5 Da embryos) (p = 0.044) and 9 dpf (n = 8 somites of 4 Wt embryos, n = 6 somites of 3 Da embryos) (p = 0.0019). Median, first and third quartiles are shown. HM, horizontal myoseptum; NT, neural tube. Scale bar = 50 μm. ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, ns, not significant.