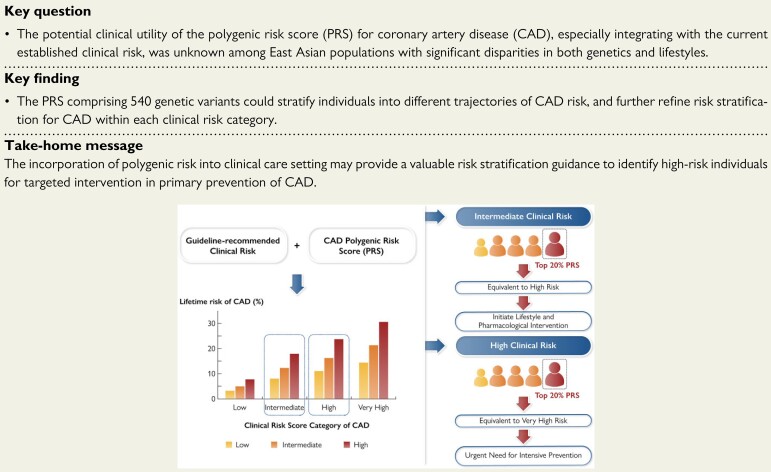
Structured Graphical Abstract.
The polygenic risk has a great potential to refine CAD risk stratification within each guideline-recommended clinical risk category and inform clinical decision making for primary prevention. Among individuals at intermediate clinical risk whose guideline-based recommendations are unclear, those with high polygenic risk should be recommended to initiate lifestyle and pharmacological intervention. Individuals with both high polygenic risk and high clinical risk urgently need intensive prevention. Combination of polygenic risk and clinical risk could promote precision prevention of CAD and reduce the disease burden, particularly considering inadequate primary prevention or statins and antihypertensive treatment in China.