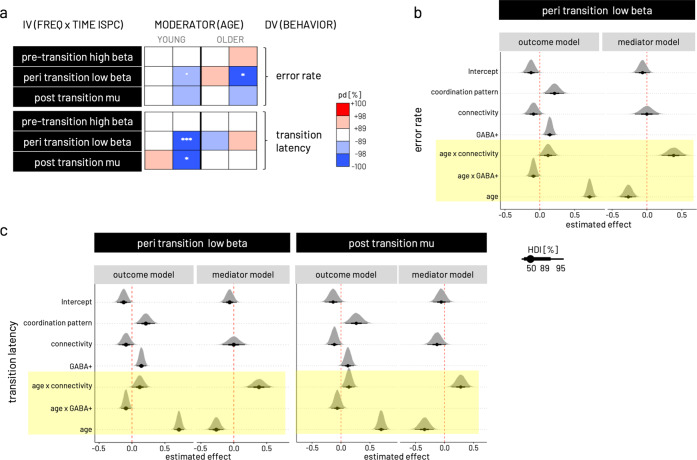
Fig. 6. Results of Bayesian moderated mediation models.
a Overview over posterior directions (pd) for indirect (mediation) effects on error rate and transition latency conditional on upper/lower quintiles of moderator age (depicted as YOUNG and OLDER) for the models estimated with the independent variable (IV) based on the three time × frequency clusters derived in the response locked ISPC analysis. Models were run separately for left and right S/M1 GABA+ as mediator. The pd can be interpreted as the maximum probability of the effect accounting for the evidence derived from the data. Color coding of pd represents likelihood (in %) and direction of effect, i.e., red shading for positive effects and blue shading for negative effects. A pd of 95, 97.5, 99.5, and 99.95% corresponds to the frequentist two-sided p-value at the thresholds 0.1˚, 0.05*, 0.01**, 0.001*** respectively. See respective Methods section for further information about effect descriptors and measures of uncertainty used in Bayesian statistics. b Probability density plots for effects of parameters in the outcome and the mediator models input to the mediation analysis. Depicted are the three models with significant mediation shown in (a). The outcome model is shown for error rate and peri transition low beta ISPC. c Outcome models are shown for dependent variable transition latency and peri-transition low beta ISPC (left) as well as post-transition mu ISPC (right). For all three models shown in (b) and (c), the mediator model is related to right S/M1 GABA+. Highlighted in yellow are the significant effects of moderator age in all three models indicated by the posterior distributions of respective parameters falling with >99.5% on one side of the red dashed vertical line. Linewidth of black horizontal bars indicates 50, 89, and 95% highest density interval [HDI] of the parameters’ effect. The Bayesian moderated mediation analysis was run based on data from N = 22 older and N = 20 younger participants.