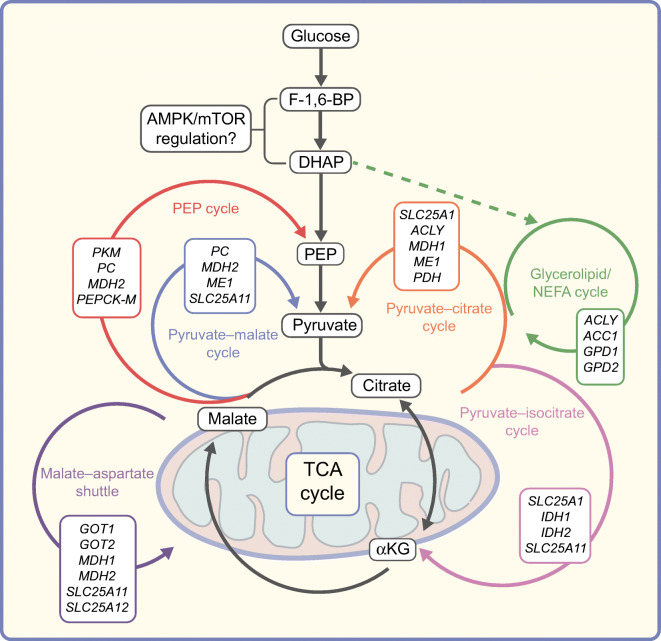
Fig. 2.
Proposed glucose-sensitive metabolic cycles in functionally mature beta cells. The metabolic processing of glucose into TCA cycle intermediates with the resultant oxidative phosphorylation pathway is a core component of canonical GSIS. However, the processing of TCA-derived metabolites throughout a multitude of mitochondrial–cytosolic cycling reactions have also been shown to be a component of mature beta cell function. Genes that form core components of each cycle are shown in boxes outlined in the colour of the relevant cycle. Glycolytic intermediates may also act in the regulation of glucose-sensitive metabolism, together with interactions with elements of cellular energy-sensing machinery. F-1,6-BP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; αKG, α-ketoglutarate. This figure is available as part of a downloadable slideset