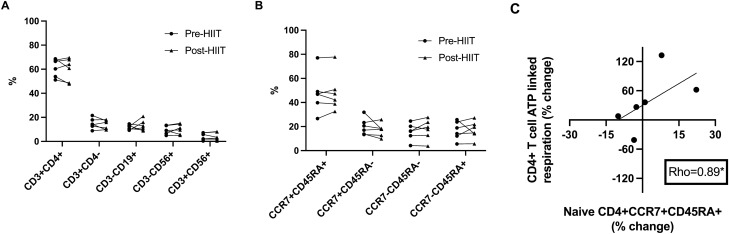
Figure 2.
Changes in RA T cell oxidative metabolism following HIIT are associated with changes in naïve T cells. (A) Graphs show changes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) peripheral CD3 + CD4 + helper T cells, CD3 + CD4- non-helper T cells, CD3-CD19 + B cells, CD3-CD56 + natural killer cells, and CD3 + CD56 + natural killer T cells following high-intensity interval training (HIIT) (subgroup n = 6; p > 0.05 for all pre-HIIT versus post-HIIT comparisons). (B) Graphs show changes in RA peripheral naïve CCR7 + CD45RA + , central memory CCR7 + CD45RA-, effector memory CCR7-CD45RA-, and terminally differentiated CCR7-CD45RA + CD4 + T cells following HIIT (p > 0.05 for all pre-HIIT versus post-HIIT comparisons). (C) Scatter plot depicts relationship between percent change in RA peripheral CD4 + T cell ATP linked respiration (y-axis) and percent change in peripheral naïve CD4 + T cells (x-axis) following HIIT. *p < 0.05 for paired t-tests and Spearman correlations.