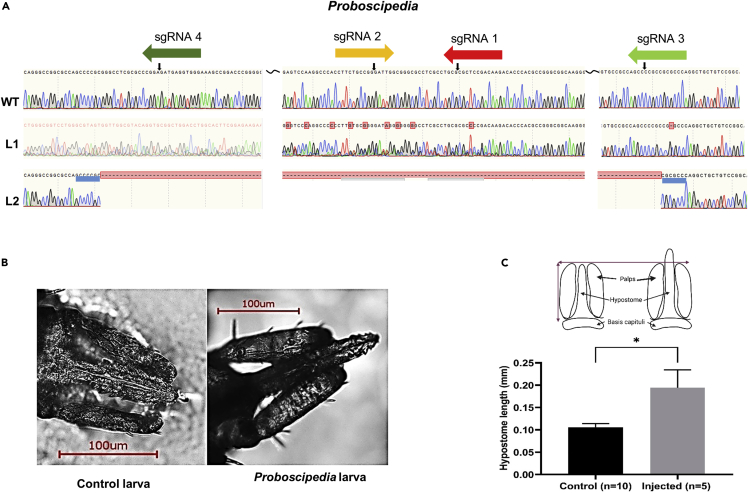
Figure 2.
Sequences of Proboscipedia G0 larvae edited by embryo injection aligned to wildtype (WT)
(A) Sequences and chromatograms of wildtype (WT), heterozygous deletion (L1), and homozygous deletion (L2). GC-rich regions flanking the homozygous deletions are underlined in blue. Black squiggly lines represent an additional deleted sequence in that region.
(B) Control and mutant larva (L1) showing extended hypostome phenotype.
(C) Illustration of tick mouthparts and measurements (top), a graph showing hypostome length in wildtype (control) and injected larvae (bottom).Data are presented as mean ±SEM. An unpaired Student’s t test was used to calculate significance ∗ = p> 0.05