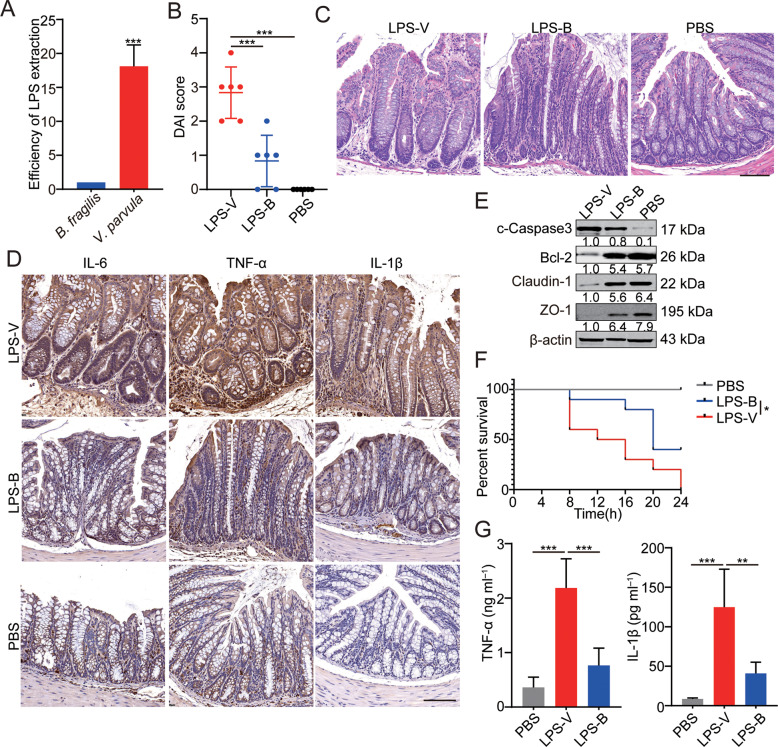
Fig. 2. The high toxic effects of LPS from V. parvula in vivo.
A The efficiency of LPS extraction from V. parvula and B. fragilis. B The disease activity index (DAI) of mice in V. parvula group is higher than that in B. fragilis or PBS group. C Representative photomicrographs showing worse histologic injury as well as more crypt abscesses and more distribution of immune cells in the distal colon of mice fed with LPS. Scale bars: 100 μm. D Higher levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) in distal colon of mice treated with LPS-V. E Western blotting assays showing more apoptosis and impaired tight junction induced by LPS-V than LPS-B or PBS in distal colon tissues. F Survival in mice (n = 10 mice/group) treated with LPS-V is shorter compared to mice treated with LPS-B or PBS in an LPS model of sepsis. G Serum concentration of pro-inflammatory factors in three groups. All data are expressed as mean ± SD. NS denotes no signification. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.