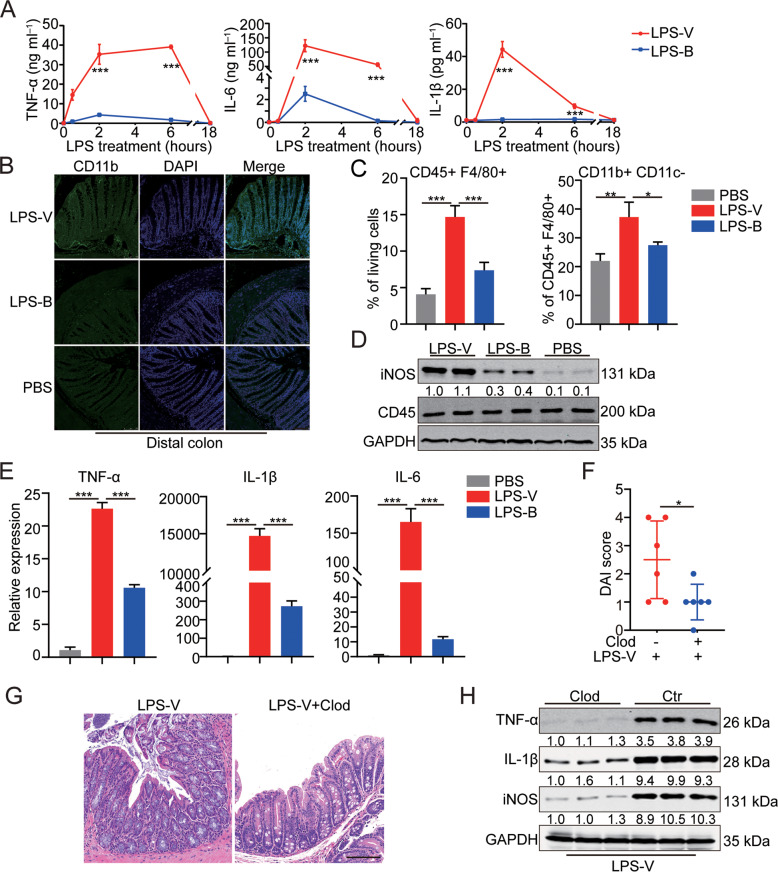
Fig. 4. LPS-V promoted the development of intestinal inflammation through activating macrophages.
A Supernatant concentration of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α) in BMDMs treated with LPS-V or LPS-B at indicated time points. B Representative photomicrographs of IF staining showing more CD11b + macrophages in mice of LPS-V group compared to LPS-B or PBS group. Scale bars: 100 μm. C Flow cytometric histograms indicating the detection of pro-inflammatory macrophages in distal colon of mice treated with LPS-V, LPS-B, or PBS. D Western blotting assays showing that LPS-V increased iNOS level in distal colon. E mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) in human macrophages treated with LPS-V, LPS-B, or PBS. F The disease activity index (DAI) of mice indicating macrophage depletion using Clod treatment alleviated the effects of LPS-V. G Representative photomicrographs showing macrophage depletion using Clod treatment alleviated the effects of LPS-V. on colon tissue. Scale bars: 100 μm. H Western blotting assays showing macrophage depletion using Clod treatment decreased IL-1β, TNF-α and iNOS level in distal colon. All data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.