Fig. 6. Summary of the experimental findings in the studies.
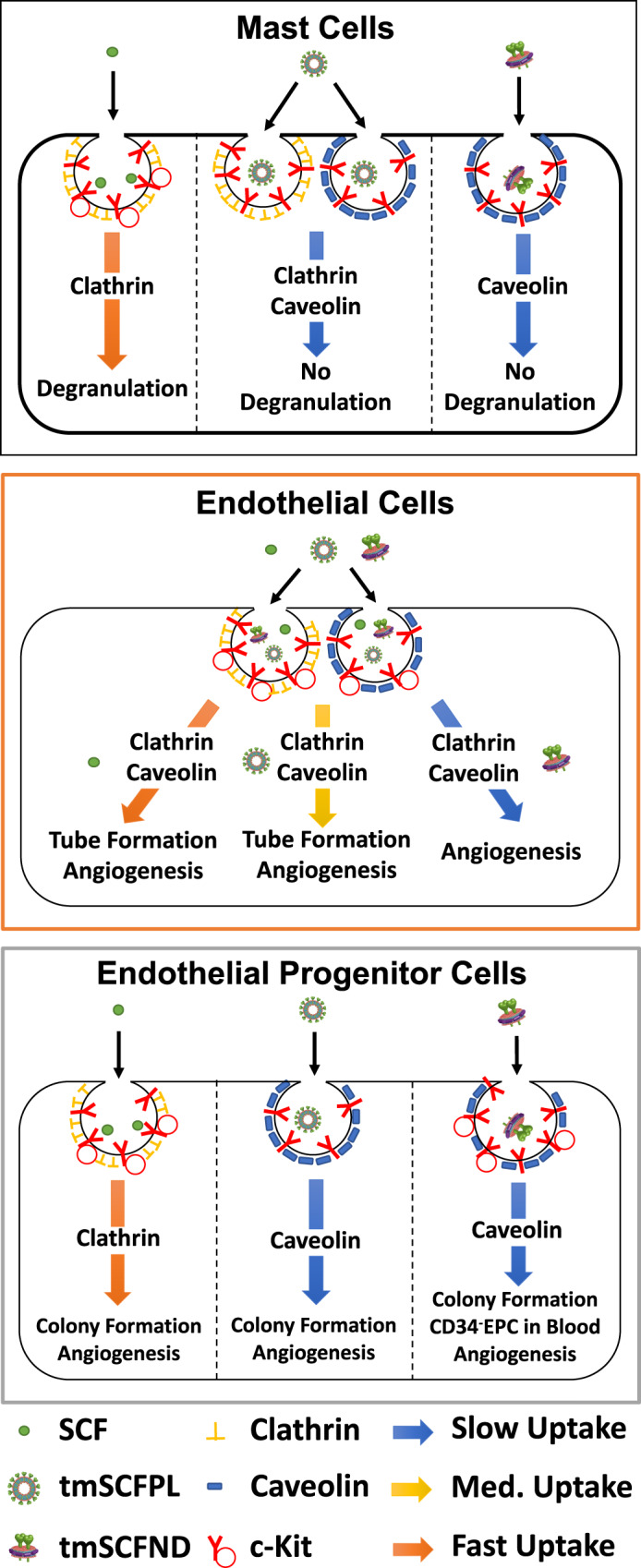
Mast cells use primarily a clathrin-mediated pathway to internalize SCF, leading to mast cell activation and anaphylaxis. In contrast, mast cells use predominantly clathrin and caveolin-mediated pathway to uptake tmSCF-based treatments and these treatments do not cause mast cell activation. Endothelial cells use both of clathrin- and caveolin-mediated pathway to uptake SCF, inducing angiogenesis in endothelial cells. Endothelial cells use both of clathrin- and caveolin-mediated pathway to internalize tmSCFPLs with medium uptake speed, triggering tube formation of endothelial cells and therapeutic angiogenesis. However, tmSCFNDs are internalized through clathrin/caveolin-mediated pathways with slow kinetics and do not induce an angiogenic response from mature endothelial cells. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) use clathrin-mediated pathway to uptake SCF, triggering colony formation of EPCs and bone marrow cell mobilization. For tmSCF-based treatments, EPCs use a caveolin-mediated pathway for internalization leading to colony formation and angiogenesis. Treatment with tmSCFNDs further induced the mobilization of CD34−CD133+ EPCs to the peripheral blood.
