FIGURE 5.
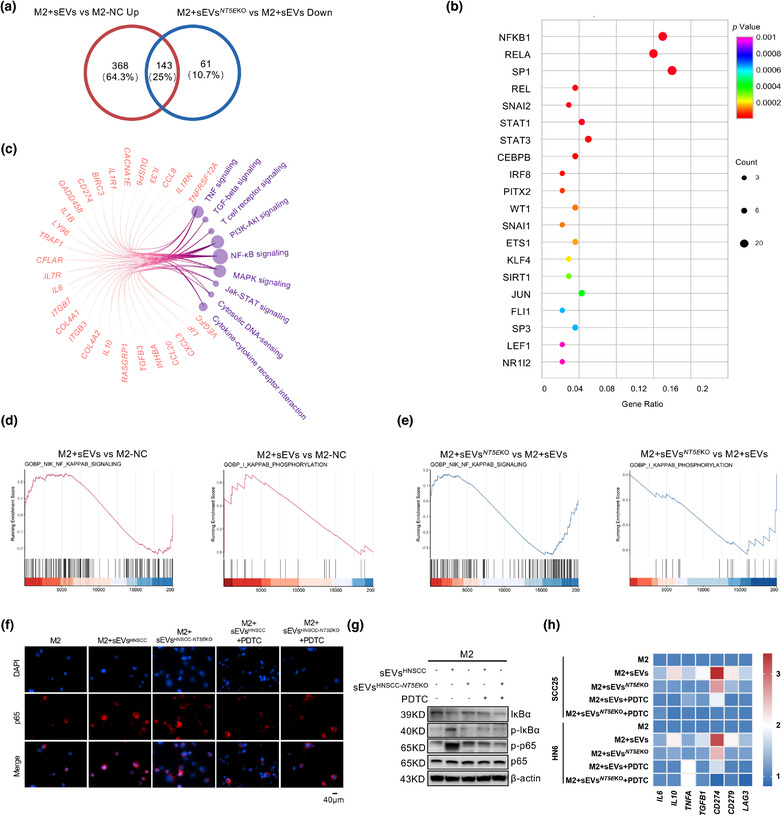
CD73 in sEVs regulates the immune functions of TAMs through NF‐κB pathway. (a) Venn diagram showing the differential expressed gene (DEG) of M2 macrophages depending on the regulation by sEVsCD73 or sEVs NT5E KO, the numbers of shared and exclusive genes were exhibited. (b) Bubble plot showing the predicted transcription factors of shared DEGs from AC. The shared DEGs and the signalling pathways which they belonged to were shown in circos gram, the number of genes was represented by node size. (d and e) GSEA analysis of up‐stream events of NF‐κB regulation. IκB phosphorylation and NIK signaling activity was measure after sEVsCD73 (up regulated) or sEVs NT5E KO (down regulated) incubation. (f) M2 macrophages were treated by HNSCC cell lines‐derived sEVs with or without CD73 for 3 h, with or without pretreatment of 100 μM PDTC for 1h. IF was applied for assessing the translocation of p65 in M2 macrophages (Scale bar = 40 μm). (g) Western blot was performed to validate the status of IκBα degradation, IκBα phosphorylation, p65 and phosphorylated p65 in M2 macrophages following treatment with sEVs or sEVs NT5E KO from HNSCC cell lines. (h) The heatmap showed the mRNA levels of IL6, IL10, TNFA, TGFB1, CD274, CD279, and LAG3 in M2 macrophages which were stimulated by HNSCC derived sEVs, the expressions were partially downregulated when sEVs NT5E KO were added, and further inhibited when pretreated with PDTC
