FIGURE 6.
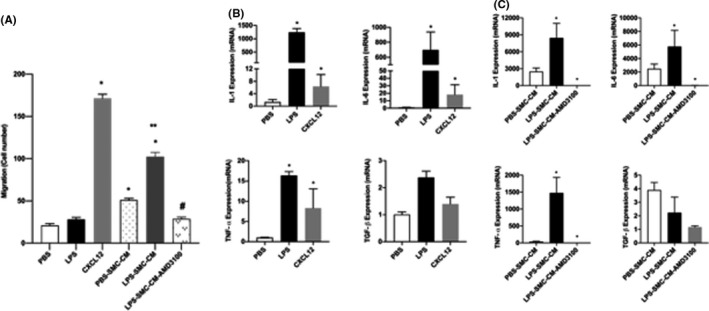
AMD3100 inhibited USMCs‐CM induced macrophage migration through CXCL12/CXCR4 signalling. (A) Macrophage attraction was determined by migration assay. Macrophages migrated significantly when treated with CXCL12 but not LPS. Conditioned medium from SMCs increased migration. Conditioned media from SMCs treated with LPS further increased migration. AMD3100 significantly inhibited macrophage migration stimulated by LPS‐treated SMC‐conditioned medium. Data are shown as a number of macrophages migrated. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM for data from two individual experiments and each experiment was performed in triplicate. *p < 0.05 versus PBS, **p < 0.05 versus PBS‐SMC‐CM and # p < 0.05 versus LPS‐SMC‐CM. (B, C) AMD3100 inhibited LPS stimulation of proinflammatory cytokines in M1 macrophage. (B) qRT‐PCR results showing significant increase in mRNA levels of IL‐1, IL‐6, TNF‐α induced by LPS or CXCL12 treatments compared with PBS. (C) qRT‐PCR results showing significant induction of IL‐1, IL‐6, TNF‐α expression stimulated by conditioned medium from smooth muscle cells treated with LPS. The effect of conditioned media on cytokine induction is blocked by AMD3100. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM for data from three individual experiments, and each experiment was performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus PBS or PBS‐SMC‐CM. IHC, immunohistochemistry; IL, inyterleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; SEM, standard error of mean; SMC‐CM, smooth muscle cell conditioned media; qRT‐PCR, quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; USMC‐CM, uterine smooth muscle cell conditioned media
