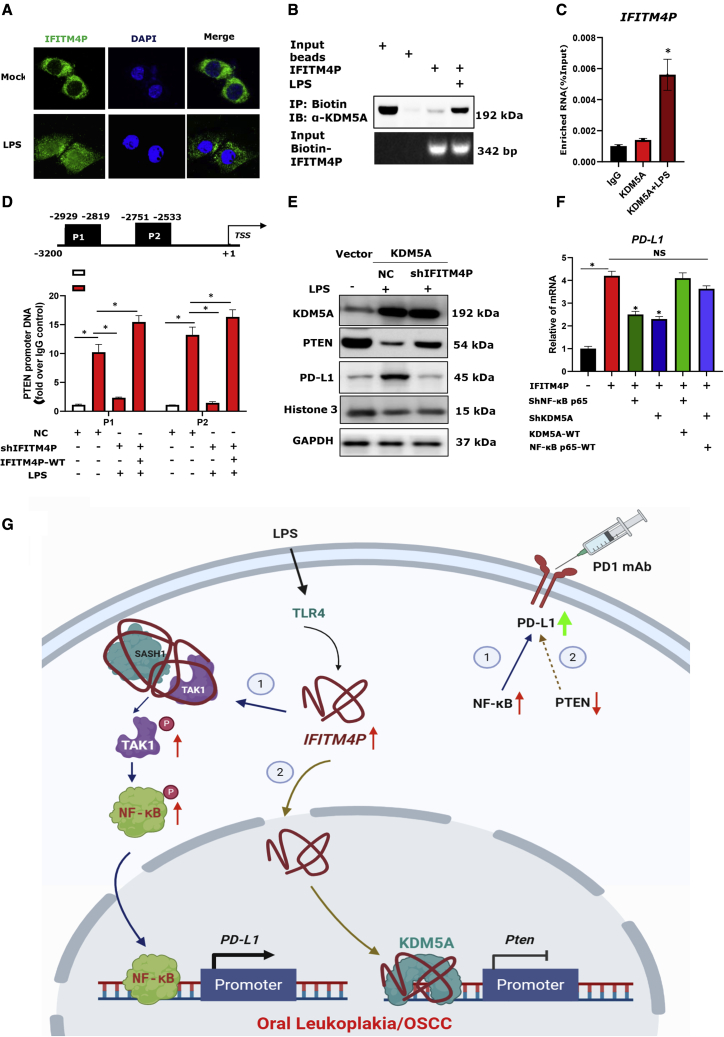
Figure 6.
Ectopic expression of IFITM4P effectively enhanced the binding of KDM5A to Pten promoter and increased PD-L1 abundance
(A) Confocal microscopy showed IFITM4P was obviously transferred from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in Leuk-1 under LPS stimulation (100 μg/mL) by FISH assays (400×). Assessment of the nuclear morphology used DAPI staining. (B) Biotin-labeled IFITM4P pull-down and WB showed that IFITM4P specifically co-precipitates with KDM5A in Leuk-1 cells upon LPS stimulation (100 μg/mL) for 12 h. Beads served as the negative control. (C) RIP assays validated the association of KDM5A with IFITM4P in Leuk-1 cells upon LPS stimulation (100 μg/mL) for 12 h. IgG antibodies served as the control. (D) ChIP analysis of the Pten promoter in Leuk-1 cells. Upper: KDM5A binding sites. Lower: ChIP assays showed that KDM5A specifically bound P1 and P2. Deletion of IFITM4P alone markedly reduced the binding of KDM5A to Pten, while transfecting the plasmid of IFITM4MP-WT in stable knockdown-IFITM4P-Leuk-1 can reduce the inhibitory effect on the binding of KDM5A to Pten. ChIP assays were performed with anti-KDM5A antibody or IgG as a control. Enriched DNA fragments flanking P1 and P2 were examined by RT-PCR assays using specific primer sets. (E) WB analysis of relative Pten mRNA expression in Vector and KDM5A-overexpressing Leuk-1 cells under LPS stimulation (100 μg/mL). (F) IFITM4P-Leuk-1 and Vector-Leuk-1 cells transiently transfected with shRNAs to NF-κB p65 or KDM5A or scrambled control (ShRNA-NC), KDM5A, or NF-κB p65 vector were treated with LPS (100 μg/mL). qRT-PCR showed a significant decrease in PD-L1 expression following the knockdown of KDM5A and NF-κB p65, while WT-KDM5A or WT-NF-κB p65 increased the expression of PD-L1. (G) Model describing the role of IFITM4P as an oncogene by increasing PD-L1 abundance in OL. Data from (C), (D), and (F) are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments; ∗p < 0.05; NS, no significant difference. WT, wild type.