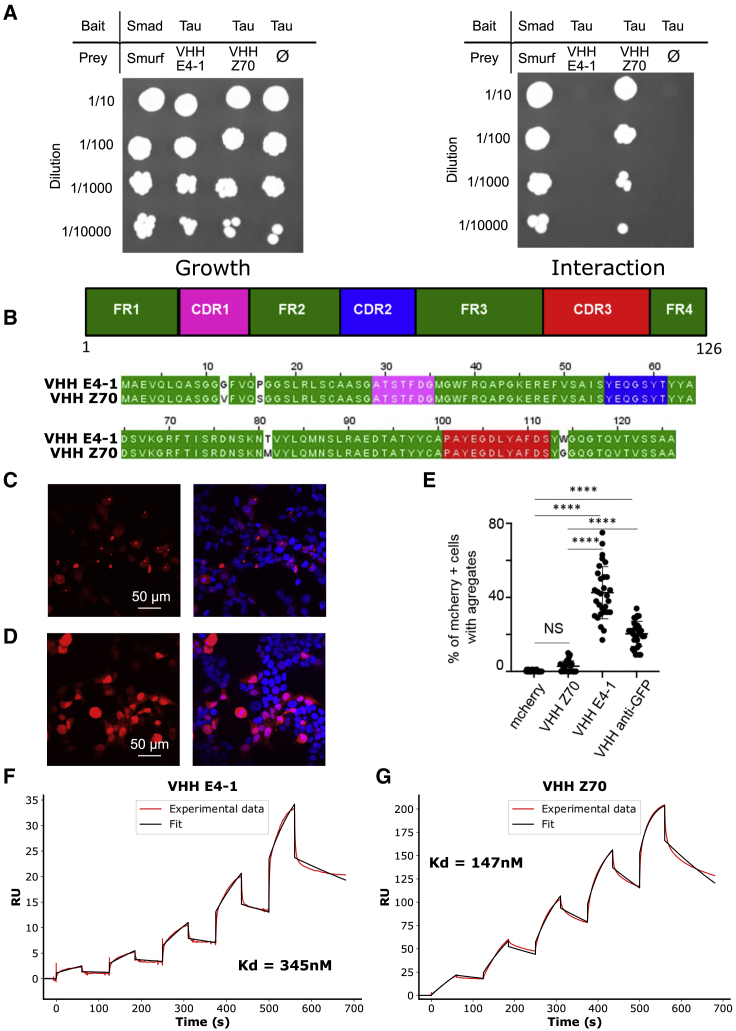
Figure 2.
VHH Z70 is optimized for intra-cellular binding and has a better affinity for Tau than VHH E4-1
(A) Results from yeast two-hybrid. A growth test on nonselective medium (left panel, lacking only leucine and tryptophan) or on selective medium (right panel, lacking leucine, tryptophan and histidine) was performed with dilution (top to bottom) of the diploid yeast culture expressing both bait and prey constructs. Positive and negative controls of interaction consist respectively of Smad/Smurf interaction42 and Tau alone (empty vector). VHH E4-1 did not interact with Tau in yeast (no growth on selective medium) whereas VHH Z70 did. (B) Domain organization of the VHHs (CDR are for complementarity-determining regions and FR for framework regions) and sequence alignment between VHH E4-1 and VHH Z70 showing four mutations in the FR: G12V, P16S, T81M, and W114G. (C, D) HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmid encoding either (C) mCherry-VHH E4.1 or (D) mCherry-VHH Z70 and mCherry or mCherry VHH anti-GFP (Figure S4). mCherry is visualized in red and nuclei in blue. The scale bar is indicated on the figure. (E) Percentage of mCherry positive cells with puncta is provided for 10 images per group and three independent experiments (30 points). Error bars indicate mean and SD of the data. ∗∗∗∗ correspond to a p value < 0.0001. (F, G) Sensorgrams (reference subtracted data) of single cycle kinetics analysis performed on immobilized biotinylated Tau, with five injections of (F) VHH E4-1 or (G) VHH Z70 at 0.125 μM, 0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1 μM, and 2 μM (n = 1). Dissociation equilibrium constant Kd were calculated from the ratio of off-rate and on-rate kinetic constants koff/kon. kon, koff, and Kd are included in the table in Figure S7. Black lines correspond to the fitted curves, red lines to the measurements.