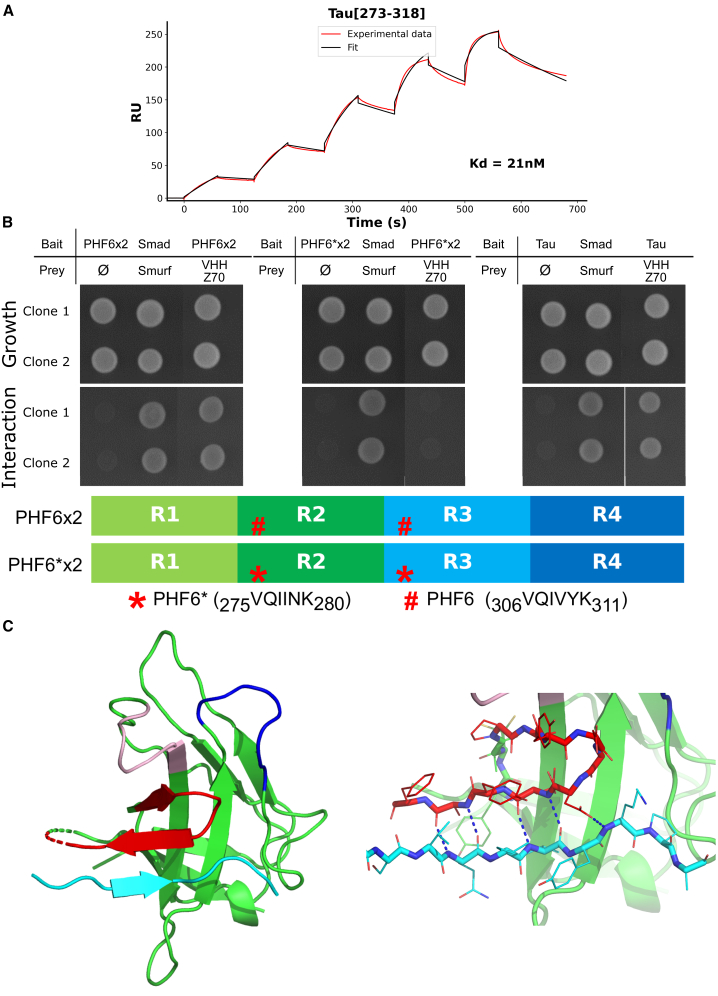
Figure 3.
The PHF6 peptide sequence is essential for VHH Z70 binding to Tau MTBD
(A) Sensorgram (reference subtracted data) of single-cycle kinetics analysis performed on immobilized biotinylated VHH Z70, with five injections of peptide Tau[273–318] fused at its N-terminus with the SUMO protein (n = 1) at 31.25 nM, 62.5 nM, 125 nM, 250 nM, and 500 nM. Tau peptide sequence and, kon, koff, and Kd are included in the table in Figure S7. Black lines correspond to the fitted curves, red lines to the measurements. (B) Results from yeast two-hybrid. The VHH are expressed as preys, with a C-terminal Gal4-activation domain fusion (VHH-Gal4AD) and Tau0N4R/MTBD as bait with a C-terminal fusion with lexA (Tau0N4R/MTBD-LexA). A growth test on nonselective medium (upper panel Growth, lacking only leucine and tryptophane) or on selective medium (lower panel Interaction, lacking leucine, tryptophane, and histidine) was performed of the diploid yeast culture expressing both bait and prey constructs. Positive and negative controls of interaction consist respectively in Smad/Smurf interaction and Tau or chimeric MTBD alone (empty vector). (C) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of the complex between VHH Z70 and the PHF6 peptide. The CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3 loops of VHH 70 are colored in pink, in dark blue, and in red, respectively. Framework regions of the VHH are represented in green and the PHF6 Tau peptide in cyan. The right panel shows the five intermolecular H-bonds (dashed blue lines) between VHH Z70 and Tau peptide. See Figure S11 for 90°-rotation view and surface representation.