Figure 3.
METTL3 regulates the transcription, stability, and translation of CTNNB1 mRNA in HeLa cells
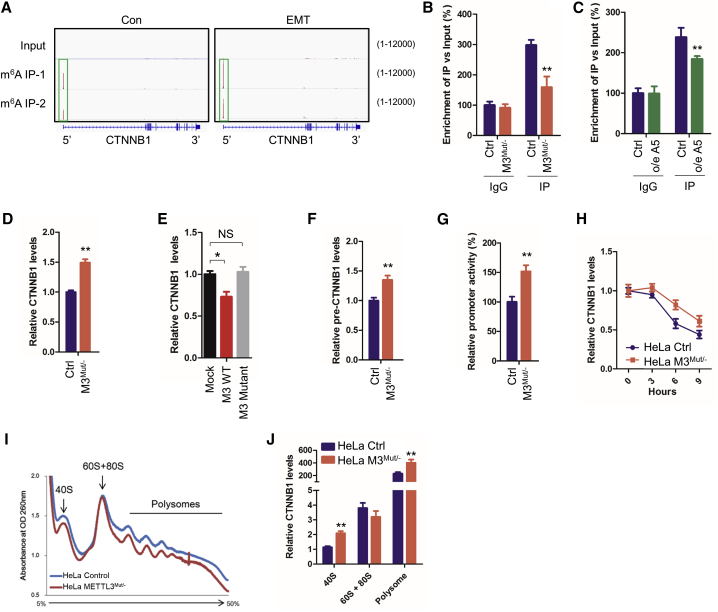
(A) m6A peaks were enriched in 5′UTR of CTNNB1 mRNA, as seen by m6A RIP-seq data (GEO: GSE112795). Squares mark the m6A peaks in HeLa cells (control [Con]) and cells undergoing EMT. (B) m6A RIP-qPCR analysis of CTNNB1 mRNA in Con and METTL3Mut/− HeLa cells. Enrichment of CTNNB1 mRNA in m6A RIP samples (IP) was normalized to IgG and sample input. (C) m6A RIP-qPCR analysis of CTNNB1 mRNA in HeLa cells transiently overexpressing empty vector pcDNA3 (Con) or pcDNA3-ALKBH5 (o/e A5). (D) Expression levels of CTNNB1 mRNA in HeLa and HeLa METTL3Mut/− cells were detected by quantitative real-time PCR. (E) Expression levels of CTNNB1 mRNA in HeLa cells overexpressing the empty vector PPB (mock), PPB-METTL3 (M3 wild type [WT]) and PPB-METTL3 mutant (M3 mutant) were detected by quantitative real-time PCR. (F) Expression levels of CTNNB1 pre-mRNA (pre-CTNNB1) in HeLa and HeLa METTL3Mut/− cells were detected by quantitative real-time PCR. (G) HeLa and HeLa METTL3Mut/− cells were co-transfected with the pGL3-Basic-CTNNB1-Fluc reporter and pRL-TK plasmids for 24 h. Results are presented as the ratios between the activity of the reporter plasmid and pRL-TK. (H) Half-life of CTNNB1 mRNA in HeLa and HeLa METTL3Mut/− cells were detected by quantitative real-time PCR. (I and J) Ribosomal profiling of HeLa and HeLa METTL3Mut/− cells (I) and the expression level of CTNNB1 mRNA in 40S, 60S, 80S, and polysome fractions (J). Data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Student’s t test; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.