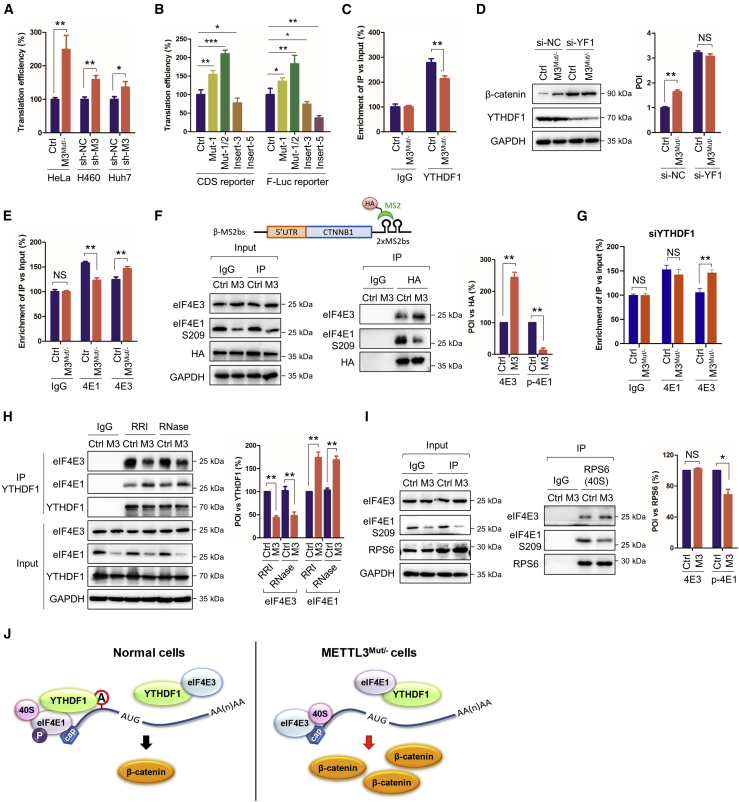
Figure 6.
YTHDF1 affects eIF4E1-mediated translation of CTNNB1
(A) Translation efficiency of CTNNB1 in HeLa, HeLa M3Mut/−, H460 sh-NC, H460 sh-METTL3, Huh7 sh-NC, and Huh7 sh-METTL3 cells was calculated as the quotient of β-catenin protein production divided by mRNA abundance.5 (B) Translation efficiency of the CDS and F-Luc reporters with mutations in Con and M3Mut/− cells was analyzed. (C) Binding between YTHDF1 and CTNNB1 mRNA in Con and M3Mut/− HeLa cells was detected by RIP-qPCR. (D) Expression levels of β-catenin in Con and M3Mut/− HeLa cells silencing YTHDF1 were detected by western blot (left) and analyzed quantitatively by ImageJ (right). (E) RIP analysis of CTNNB1 mRNA in Con and M3Mut/− HeLa cells was performed with antibodies against eIF4E1 (4 E1) and eIF4E3 (4 E3), respectively. (F) Interactions between CTNNB1 mRNA (β-MS2bs) and eIF4E1 S209 or eIF4E3 in Con and M3Mut/− HeLa cells were detected by IP (left) and analyzed quantitatively (right). (G) RIP analysis of CTNNB1 mRNA in Con and M3Mut/− HeLa cells silencing YTHDF1 was performed with antibodies against eIF4E1 (4E1) and eIF4E3 (4E3), respectively. (H) Interactions between YTHDF1 and eIF4E1 or eIF4E3 in Con and M3Mut/− HeLa cells treated with RNase inhibitor (RRI) or RNase were detected by IP. (I) Interactions between 40S and eIF4E1 S209 or eIF4E3 in Con and M3Mut/− HeLa cells were detected by IP (left) and analyzed quantitatively (right). (J) Proposed mechanism of how YTHDF1 controls canonical and non-canonical translation of CTNNB1. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Student’s t test; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.