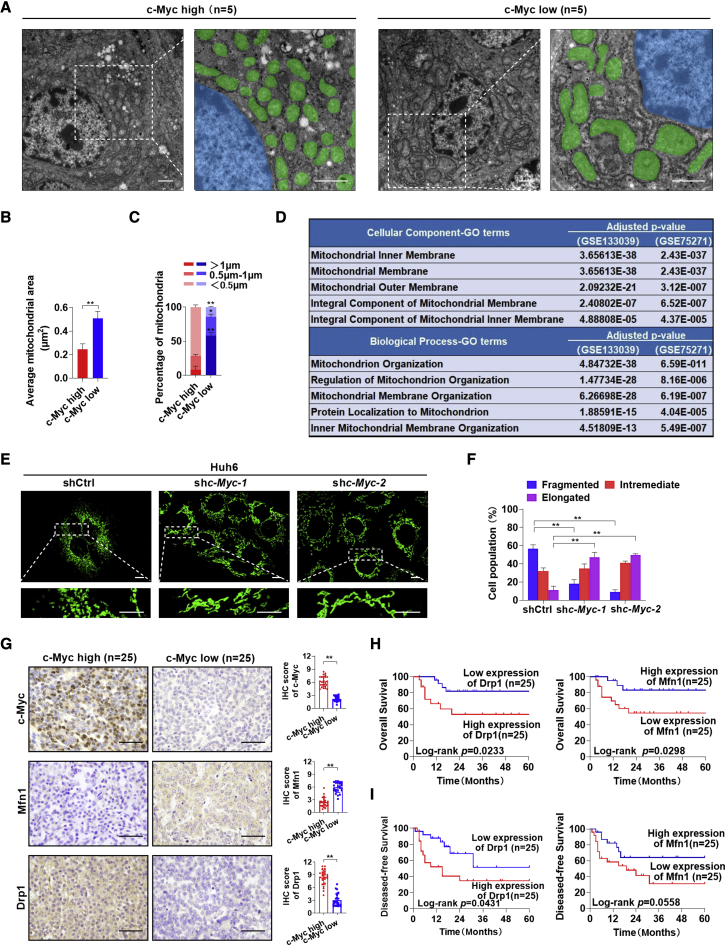
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial fragmentation is induced by c-Myc overexpression in hepatoblastoma and is associated with poor prognosis
(A) Representative TEM images of mitochondrial morphology in hepatoblastoma (HB) tissues with high (n = 5) or low (n = 5) expression levels of c-Myc. Scale bars: 1 μm. Mitochondria and nucleus were pseudo-colored green and blue. (B and C) The average area (B) and length (C) distributions of mitochondria were analyzed from five random fields (120 μm2) approximately equaling the low magnification images of TEM in each group samples. (D) Cellular component terms and biological process terms enriched by the differentially expressed genes between HB tissues with high and low c-Myc expression. (E) Representative confocal microscopy images of mitochondria in Huh6 cells with or without c-Myc knockdown. Scale bars: 10 μm. shc-Myc-1 and shc-Myc-2, shRNA against c-Myc; shctrl, control shRNA. (F) Morphology distribution of mitochondria was analyzed in Huh6 cells with different treatment as indicated. (G) Representative immunohistochemical (IHC) staining images of c-Myc, Mfn1, and Drp1 in HB tissues with high (n = 25) and low (n = 25) c-Myc expression. Scale bar: 50 μm. (H and I) Kaplan-Meier curve analysis of overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in HB patients by the expression of Drp1 and Mfn1. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.