Fig. 4.
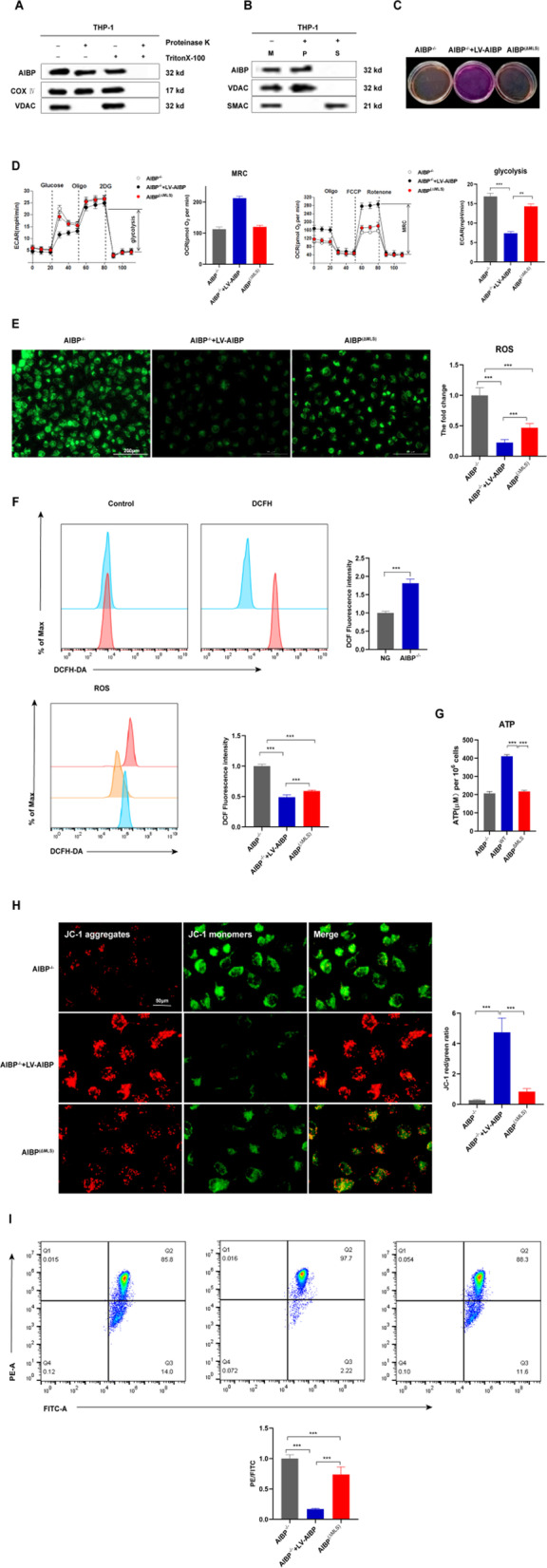
Mitochondrial AIBP maintains mitochondrial OXPHOS. A–B Alkaline extraction was performed using Na2CO3 to treat the mitochondrial fraction isolated from THP-1 cells. Both the soluble protein fraction (S) and integral membrane protein fraction (P) of AIBP were used for Western blot analysis. (M) Untreated control mitochondrial sample (n = 5). C Phenol red-containing cell culture media from AIBP−/−, AIBP−/− + LV-AIBP and AIBP(ΔMLS) BMDMs (n = 5). D BMDMs were seeded in Seahorse plates and incubated for 24 h. During the extracellular flux analysis, cells were sequentially treated with oligomycin (OM), carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP), and rotenone (ROT) plus antimycin A (AA) to assess OXPHOS parameters related to the OCR levels or with glucose, oligomycin (OM), and 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) to determine glycolysis parameters related to the ECAR levels. E Fluorescence images of BMDMs stained with 10 μM DCF-DA. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation was identified by measuring the DCF-DA intensity under a fluorescence microscope. Scale bar: 200 μm. F Flow cytometry analysis to detect ROS production. (G) ATP levels in AIBP−/−, AIBP−/− + LV-AIBP and AIBP(ΔMLS) BMDMs. H Cells were stained with JC-1. In nondamaged cells, JC-1 forms red-emitting aggregates in the mitochondrial matrix. A loss of red fluorescence and an increase in cytoplasmic green-emitting monomers signal the disruption of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔΨm). Scale bar: 50 μm. I ΔMφ was measured using flow cytometry after staining BMDMs with tetramethylrhodamine methylester (TMRM). Data are presented as the means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. One-way ANOVA followed by the Newman–Keuls test
