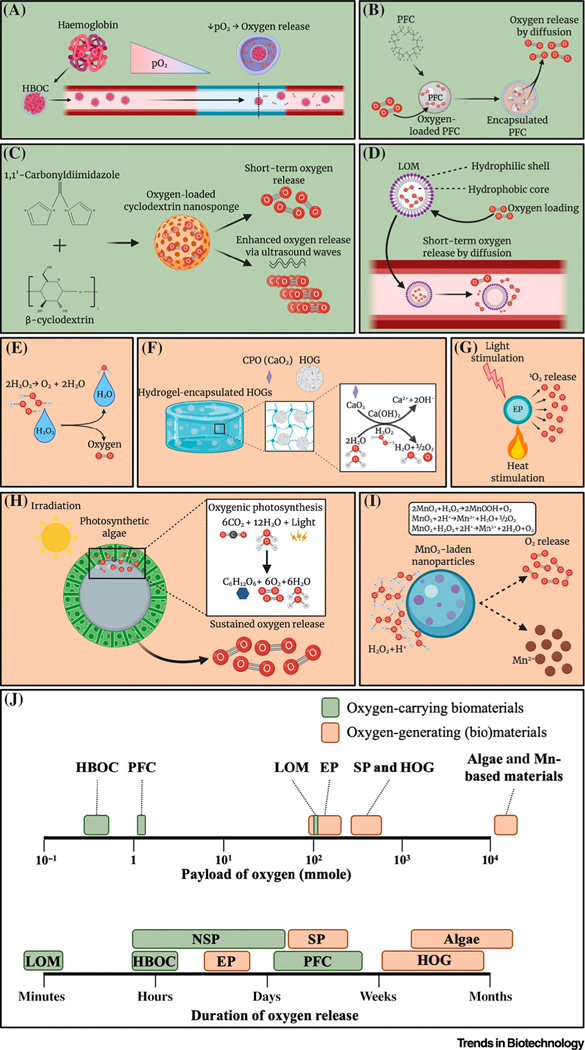
Figure 2.
Key Figure Oxygen Release from Oxygen-Carrying and Oxygen-Generating Biomaterials (OCBs and OGBs)
(A–I) Oxygen-release mechanism of various OCBs and OGBs: (A) haemoglobin-based oxygen carrier (HBOC), (B) perfluorocarbon (PFC), (C) nanosponge, (D) lipid-based oxygen microbubble, (E) liquid peroxide, (F) solid peroxide (SP), (G) endoperoxide, (H) algae-based biomaterials, and (I) manganese-based materials. (J) Comparison of oxygen payload [35,38,40,53,102–104] and duration of OCBs and OGBs [23,24,31,32,35,37,39,47,53–55,57,66,102,105–110]. Abbreviations: 1O2, Singlet oxygen; CPO, calcium peroxide; EP, endoperoxide; HOG, hydrophobic oxygen generator; LOM, lipid-based oxygen microbubble; Mn, manganese; MnO2, manganese (IV) oxide; pO2, partial pressure of oxygen. Figure created with BioRender.com.