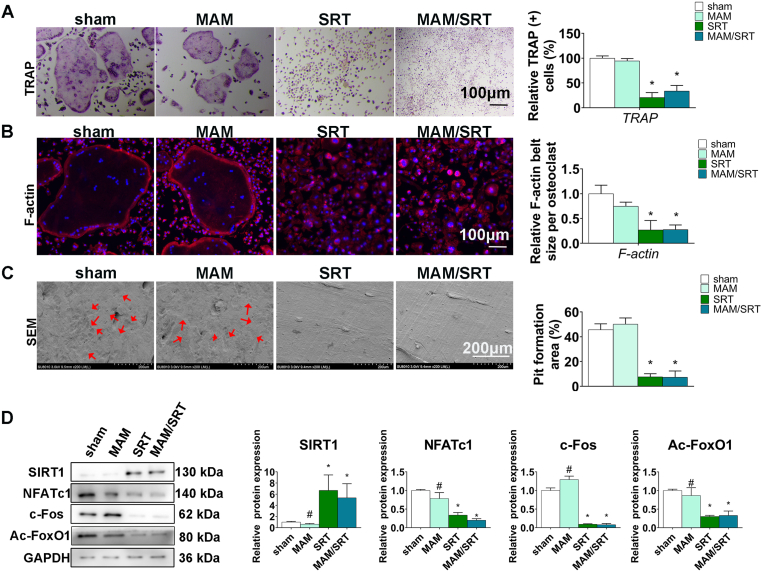
Fig. 6.
MAM/SRT suppressed the osteoclastogenesis in vitro. (A) TRAP staining for osteoclasts formation at day 5 after osteoclastic induction. Scale bars = 100 μm *p < 0.05 vs. sham group. #p < 0.05 vs. MAM/SRT group. (B) Immunofluorescence for RANKL-induced F-actin ring formation in vitro. The average F-actin belt size were normalized with sham group. Red represents F-actin labeling with phalloidin and blue represents the nucleus stained with DAPI. Scale bars = 100 μm *p < 0.05 vs. sham group. #P < 0.05 vs. MAM/SRT group. (C) Scanning electron microscope for bone resorption pits by osteoclasts. Scale bars = 200 μm *p < 0.05 vs. sham group. #p < 0.05 vs. MAM/SRT group. (D) Expression levels of SIRT1, NFATc1, c-Fos and acetylated FoxO1 (Ac-FoxO1) were determined by WB analysis at day 3 of osteoclastic differentiation. Protein expression levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, and one of three independent experiments is shown. *p < 0.05 vs. sham group. #p < 0.05 vs. MAM/SRT group.