Figure 6:
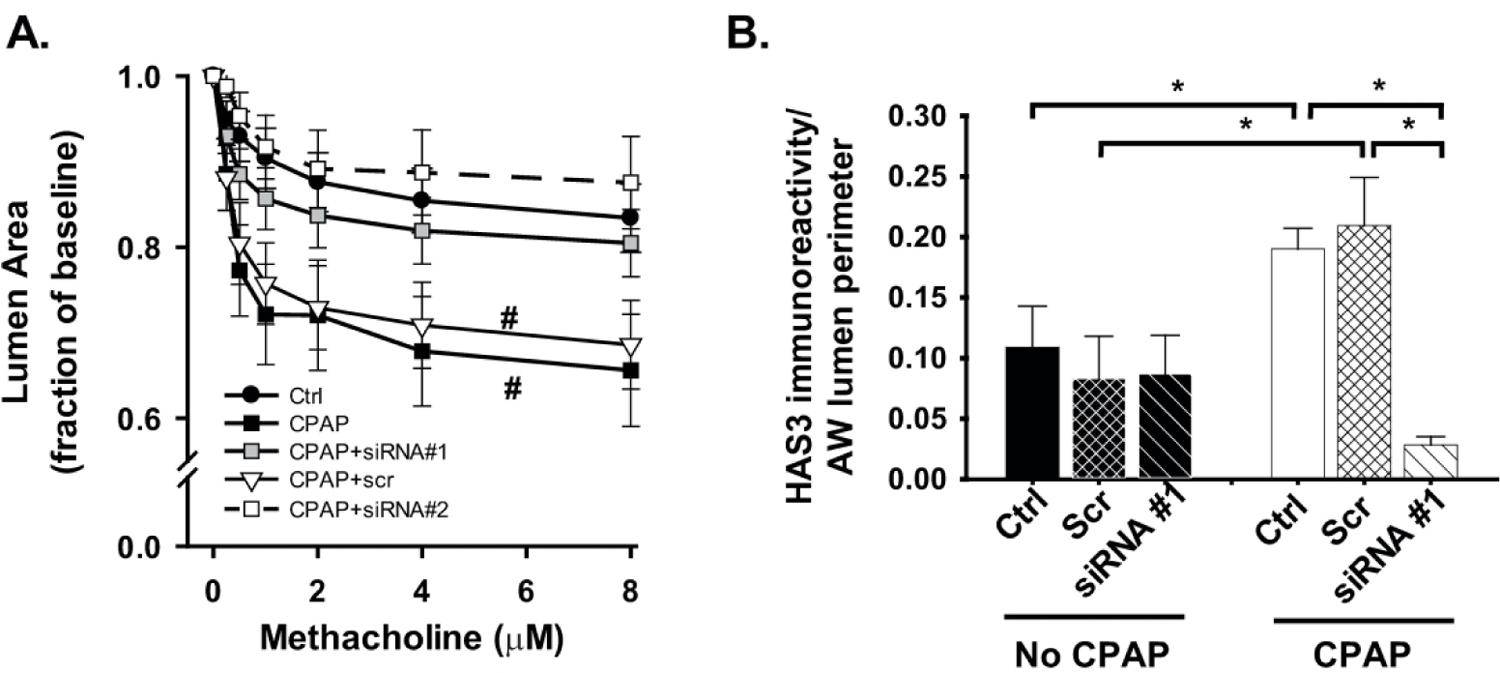
Effects of siRNA treatment on (A) CPAP-induced AW reactivity and (B) epithelial HAS3 expression in P21 day old male mice, two weeks following neonatal CPAP (6 cmH2O). Treatment groups comprise in vitro exposure (48 hrs incubation) of two different siRNAs targeted to HAS3 with a scrambled siRNA sequence. Note the increased AW reactivity following CPAP is reversed by siRNA treatment (A, siRNA#1 and #2), which was associated with decreased (vs CPAP) epithelial HAS3 expression (B). For clarity, scramble and siRNA data for control animal AW reactivity are not shown (A) and only siRNA #1 was used to show knock-down of HAS3 expression (B). #p<0.05 in the slope of the response vs Ctrl mice. N = 5–6 animals per group, 2–3 AWs/animal; values means ± SEM. Representative images from (B) are shown in Figure S3.
