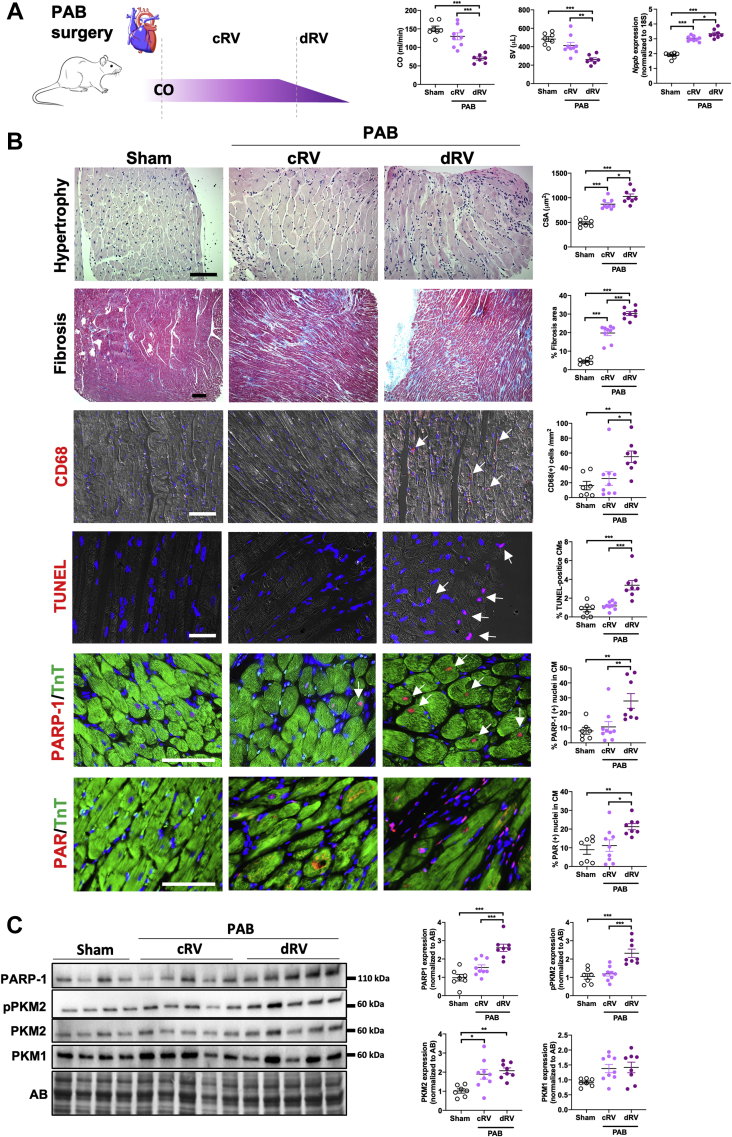
Figure 2.
Increased Expression and Activity of PARP1 and PKM2 in Decompensated Right Ventricles From PAB Rats
(A) Schematic representation of categorization of pulmonary artery banding (PAB) rats on the basis of hemodynamic status assessed using echocardiography and relative messenger RNA levels of Nppb. PAB rats underwent right heart catheterization at different time points over a period of 6 weeks, starting 2 weeks after PAB surgery. A group of sham-operated rats was used to define normal cardiac index (CO) and stroke volume (SV). PAB rats were subsequently classified into cRV or dRV groups on the basis of hemodynamic data. The relative expression levels of Nppb were used to validate the classification. (B) Representative images and corresponding quantification of RV sections from sham-operated (n = 7) and PAB-operated rats classified as cRV (n = 9) or dRV (n = 8) stained with hematoxylin and eosin (cardiomyocyte cell surface area), Masson’s trichrome (fibrosis), CD68 (infiltration of macrophages), or TUNEL (apoptosis) or double-labeled for TnT and either PARP1 or PAR. (C) Representative western blots and quantification of PARP1, pPKM2, PKM2, and PKM1 in right ventricles from rats subjected to PAB or sham surgery. Sham, n = 7; cRV, n = 9; dRV, n = 8. Scale bars, 50 mm. Arrowheads denote positive cells. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Scatter dot plots show individual values and mean ± SEM. Comparisons were made using 1-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey multiple-comparison tests or nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis tests. Abbreviations as in Figure 1.