Optimization of the reaction conditionsa.
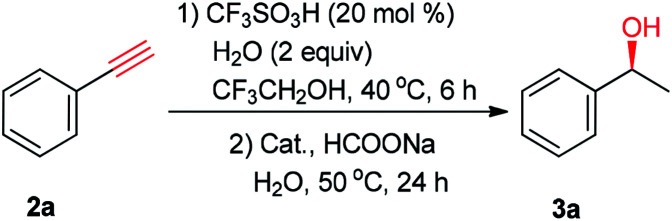
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Cat. | Hydrogen source | Yield (%) | ee (%) |
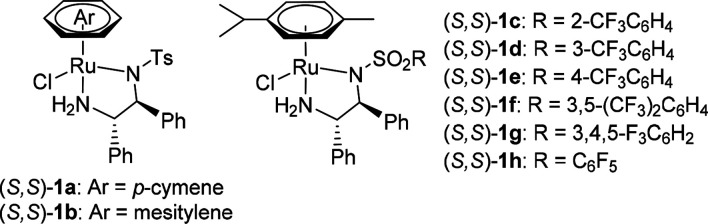
| 1 | (S,S)-1a | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 41 | 93 |
| 2 | (S,S)-1b | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | <5 | — |
| 3 | (S,S)-1c | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 80 | 87 |
| 4 | (S,S)-1d | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 83 | 96 |
| 5 | (S,S)-1e | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 78 | 79 |
| 6 | (S,S)-1f | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 79 | 94 |
| 7 | (S,S)-1g | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 84 | 94 |
| 8 | (S,S)-1h | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 95 | 97 |
| 9b | (S,S)-1h | HCOONa (5 equiv.) | 24 | 95 |
| 10c | (S,S)-1h | HCOOH/NEt3 (5:2) | 0 | — |
| 11c | (S,S)-1h | HCOOH/NEt3 (1.1:1) | 46 | 95 |
| ||||
Reaction conditions: phenylacetylene (2a; 5 mmol), CF3SO3H (20 mol%), H2O (2 equiv.), CF3CH2OH (2 mL), 40 °C, 6 h; then 0.5 mol% catalyst, hydrogen source (5 equiv.), and H2O (2 mL) were added, 50 °C, 24 h. The yield was determined by GC with an internal standard (mesitylene). The ee values were determined by HPLC analysis.
Hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP) was used as a solvent.
0.5 mL of HCOOH/NEt3 mixture was used, the data in the brackets are molar ratio.
