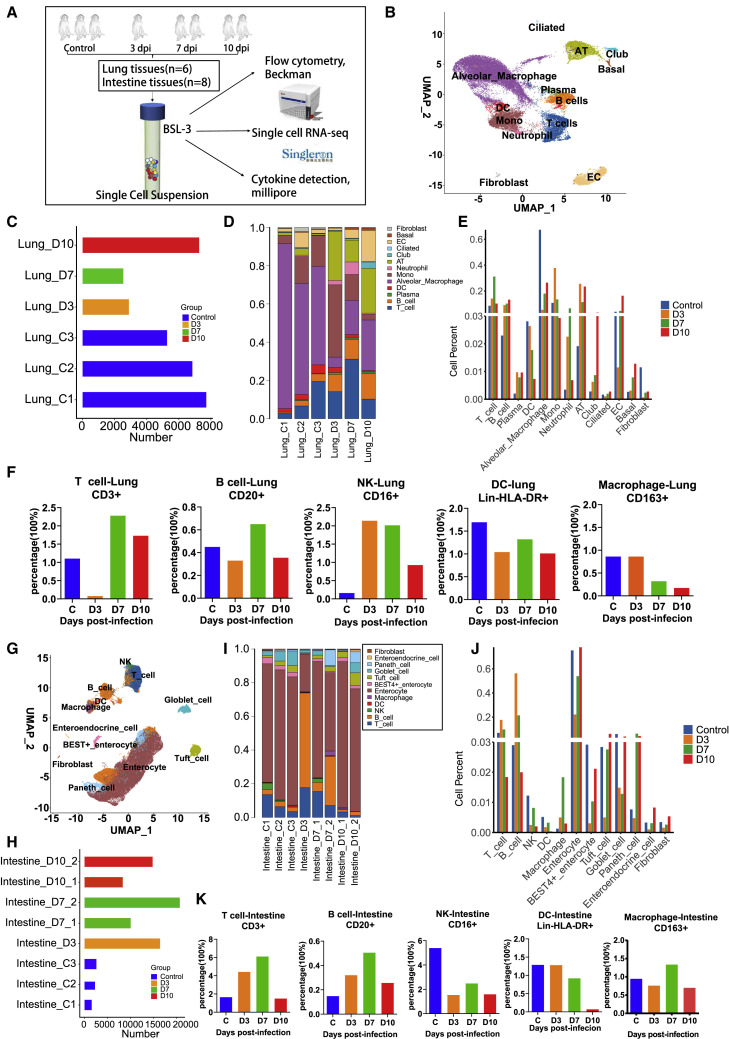
Figure 2.
Global analysis of different immune and tissue cells in SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaques
(A) Experimental workflow showing assays performed on SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaque lung and intestinal tissues at 3, 7, and 10 dpi. Tissue samples were collected from eight rhesus macaques, including three healthy controls and five infected monkeys (one euthanized at 3 dpi, two at 7 dpi, and two at 10 dpi). Two of eight lung tissue samples did not pass pre-machine quality control. scRNA-seq, flow cytometry analysis, and cytokine detection were performed in eight intestinal tissue samples and six lung tissue samples for further analysis.
(B) Identification of different cell clusters across all lung samples (n = 6).
(C) Bar plot shows the cell number of each sample for monkey lung tissues (n = 6).
(D) Cell cluster frequency shown as the fraction of total cells for each infected macaque in lung tissues (n = 6) at different infection time points.
(E) Dynamic changes in each cell cluster frequency on 3 (n = 1),7 (n = 1), and 10 (n = 1) dpi in lung tissues. Three healthy animals were regarded as the control. The average fraction of cells is shown at different infection time points.
(F) Frequency of major immune cell subsets displayed as an average percentage on 3 (n = 1), 7 (n = 1), and 10 (n = 1) dpi in lung samples by flow cytometry. Three healthy animals were regarded as the control.
(G) Identification of different immune and tissue cell clusters across all intestinal samples (n = 8).
(H) Bar plot shows the cell frequency of each sample for intestinal tissues (n = 8).
(I) Cell cluster frequency shown as the fraction of total cells for each infected macaque in intestinal tissues (n = 8)at different infection timepoints.
(J) Dynamic changes in each cell cluster frequency on 3 (n = 1), 7 (n = 2), and 10 (n = 2) dpi in small intestinal tissues. Three healthy animals were regarded as the control. The average fraction of cells is shown at different infection time points.
(K) Frequency of major immune cell subsets displayed as an average percentage on 3 (n = 1), 7 (n = 2), and 10 (n = 2) dpi in gut samples by flow cytometry. Three healthy animals were regarded as the control.
See also Figure S1.